🤔
Contracts • Excuse of Non-Performance
K#134
Legal Definition
A condition subsequent is a condition that occurs after the start of performance and excuses performance.
Plain English Explanation
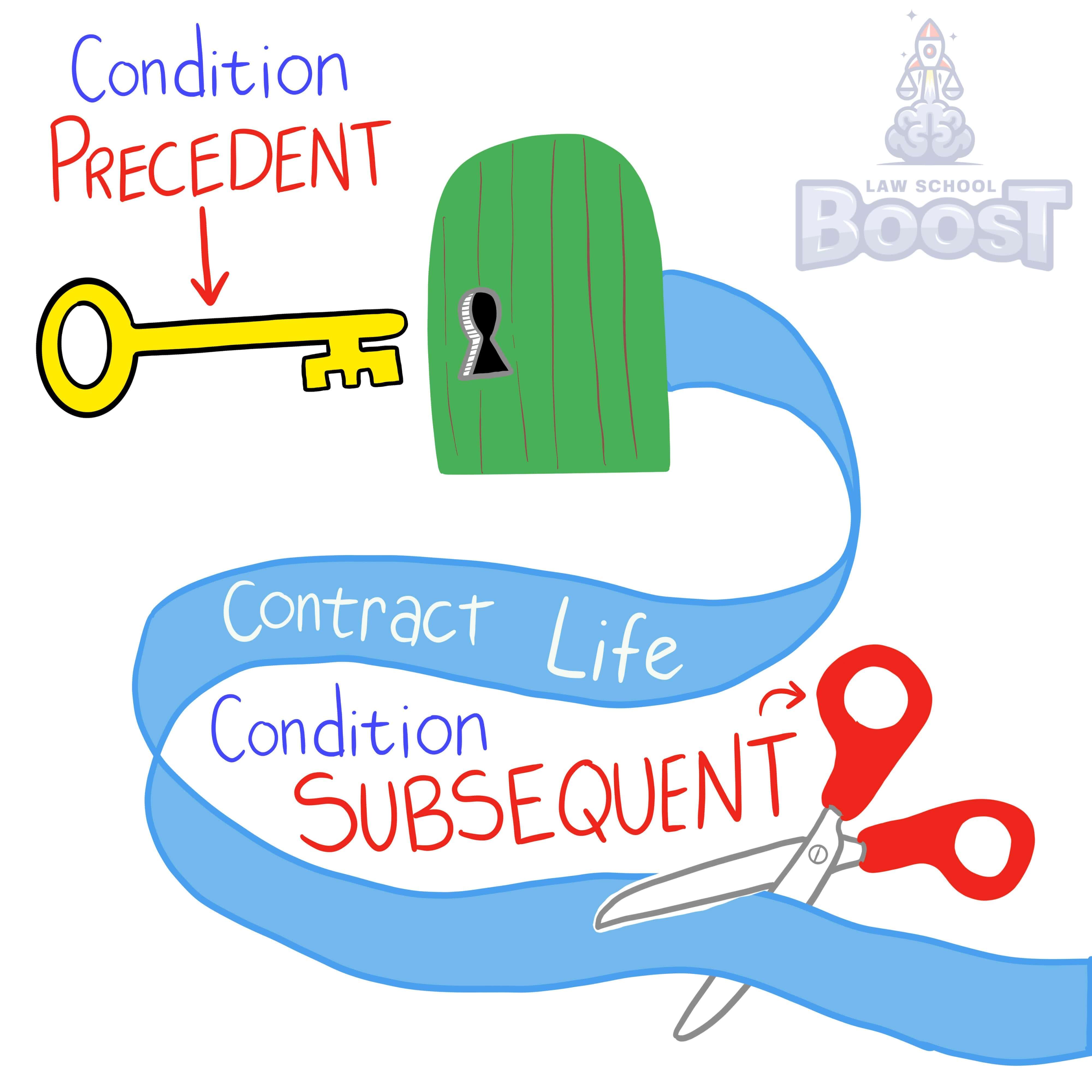
A condition precedent is a condition that must precede (or "happen before") the contract forms. It is the trigger that causes the contract to form and become binding.
Contrast this to a condition subsequent, which is a condition that happens after the contract forms. It is a trigger that, when it occurs, will change the terms of the contract (or possibly even kill the contract).
Contrast this to a condition subsequent, which is a condition that happens after the contract forms. It is a trigger that, when it occurs, will change the terms of the contract (or possibly even kill the contract).
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Bob tells Sam, "If my wife agrees, I will purchase 100 tacos from your taco cart." Sam says, "Deal." Result: Bob's wife agreeing to the deal is a condition precedent because in order for a contract to form, Bob's wife must agree. No agreement = no satisfaction of the condition = no contract formation.
Hypo 2: Bob tells Sam, "Due to the pandemic, I'd like to purchase enough tacos to fill my freezer, so I will buy 10 tacos from you every day until my freezer is full." Sam says, "Deal." Result: Here, a contract has been formed. Bob has agreed to buy 10 tacos from Sam every day, and Sam has agreed to provide 10 tacos to Bob every day. However, this contract is subject to a condition subsequent, which is "until my freezer is full." In other words, Bob is obligated to keep buying 10 tacos every day until his freezer is full. Once his freezer is full, the contract terminates.
Hypo 2: Bob tells Sam, "Due to the pandemic, I'd like to purchase enough tacos to fill my freezer, so I will buy 10 tacos from you every day until my freezer is full." Sam says, "Deal." Result: Here, a contract has been formed. Bob has agreed to buy 10 tacos from Sam every day, and Sam has agreed to provide 10 tacos to Bob every day. However, this contract is subject to a condition subsequent, which is "until my freezer is full." In other words, Bob is obligated to keep buying 10 tacos every day until his freezer is full. Once his freezer is full, the contract terminates.
Visual Aids

Related Concepts
How do courts treat checks tendered as payment in full?
How does a novation compare to a delegation?
How does a subsequent law or regulation affect performance of the contract?
How does the death of a party affect performance of the contract?
How is performance affected when the subject matter of the contract is damaged or destroyed?
How may a party eliminate express conditions?
Under common law, is late performance a material breach?
Under common law, when is counter-performance excused?
Under common law, when may a breaching party recover in a divisible contract?
Under contract law, what is a modification?
What are conditions precedent?
What are express conditions?
What are the consequences of impossibility or impracticability under the UCC?
What happens if a contract is divisible and a party performs one of the units of the contract?
What is an accord and satisfaction?
What is a novation?
What is excuse due to anticipatory repudiation?
What is excuse due to improper performance?
What is excuse due to insecurity about other party's performance?
What is excuse due to other party's non-performance?
What is frustration of purpose?
What is impracticability?
What is required to retract an anticipatory repudiation?
What is rescission?
What is the doctrine of impossibility?
What level of compliance is required to satisfy an express condition?
What options does the non-breaching party have in response to an anticipatory repudiation?
When is a contract divisible?


