‼️
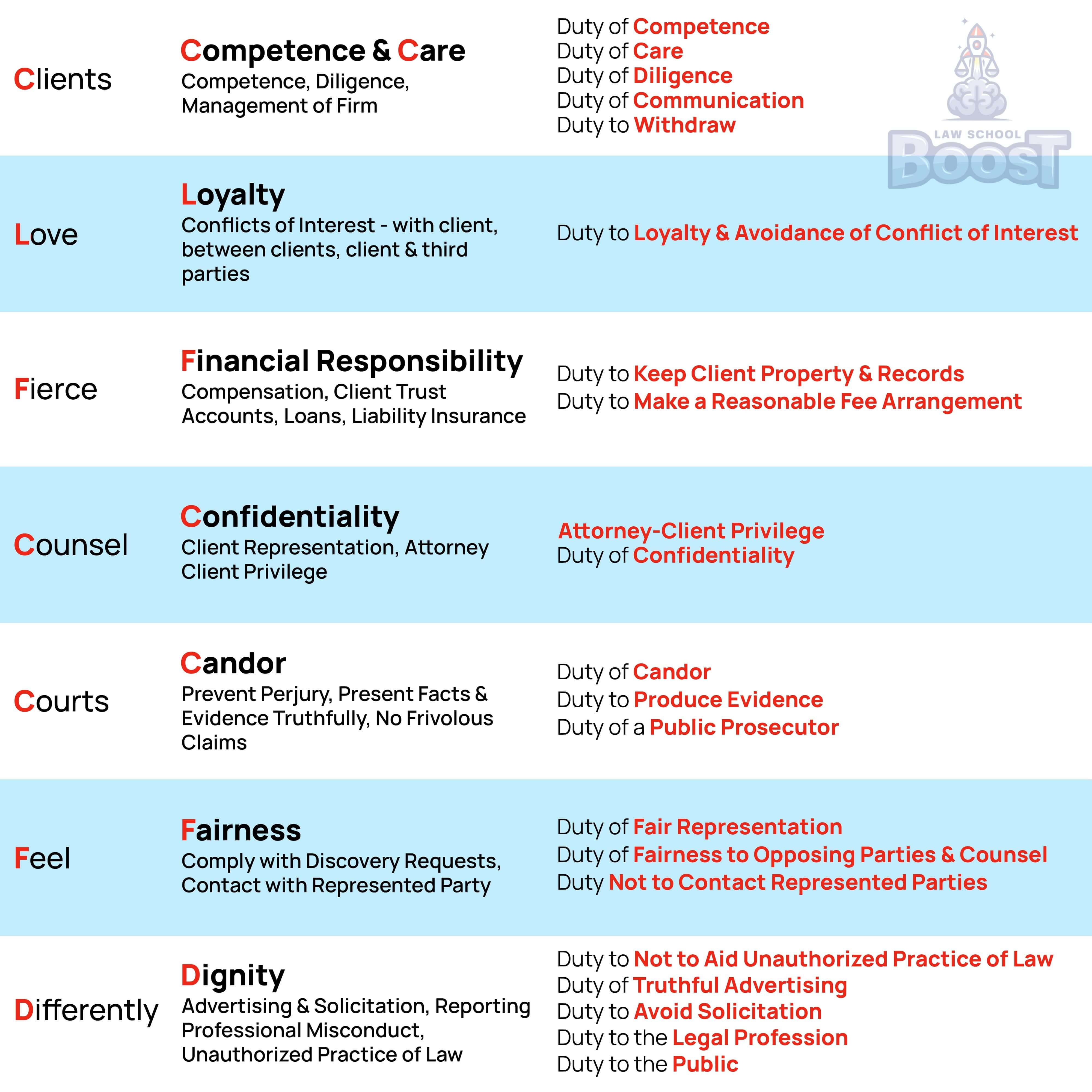
Prof Responsibility • Competence
PR#051
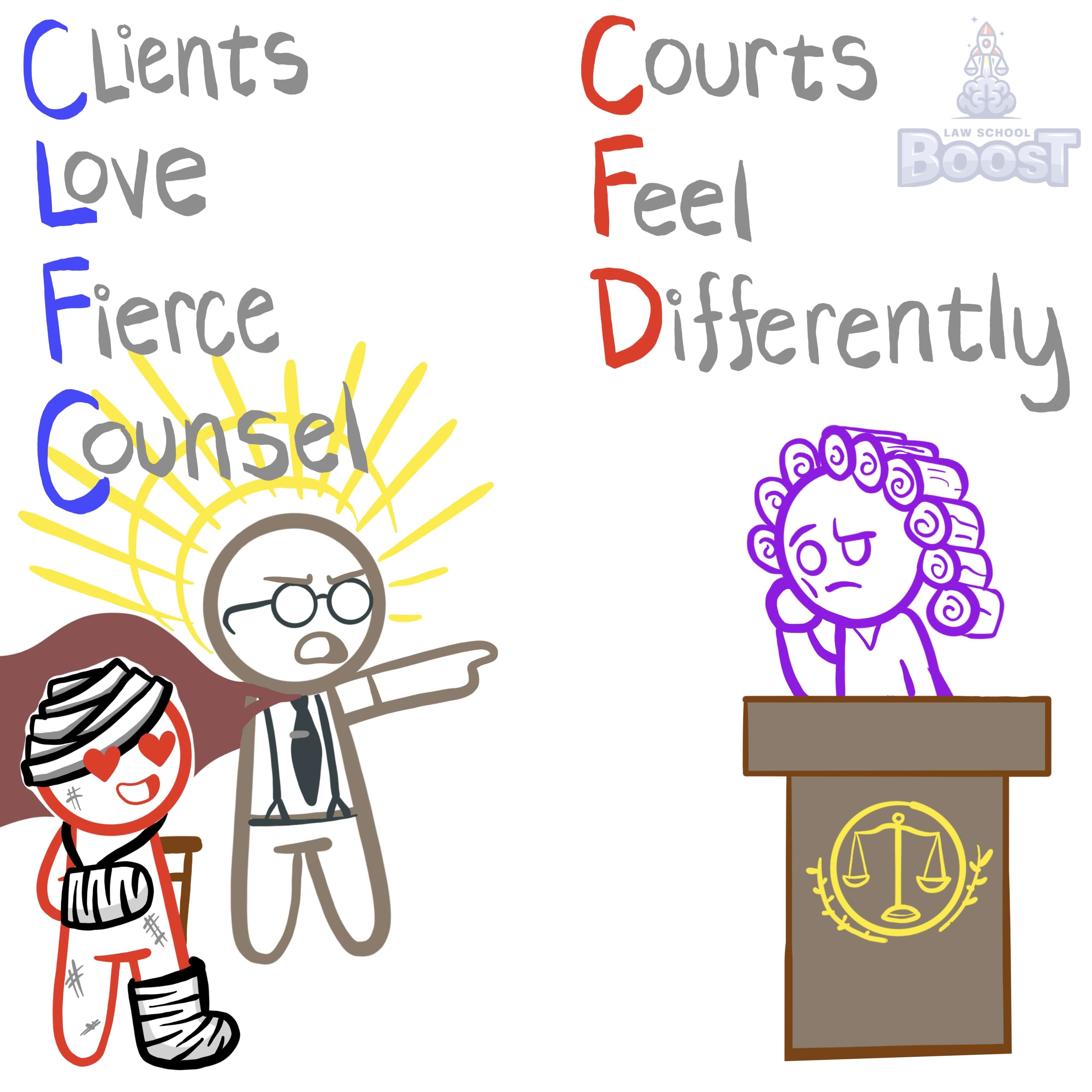
Legal Definition
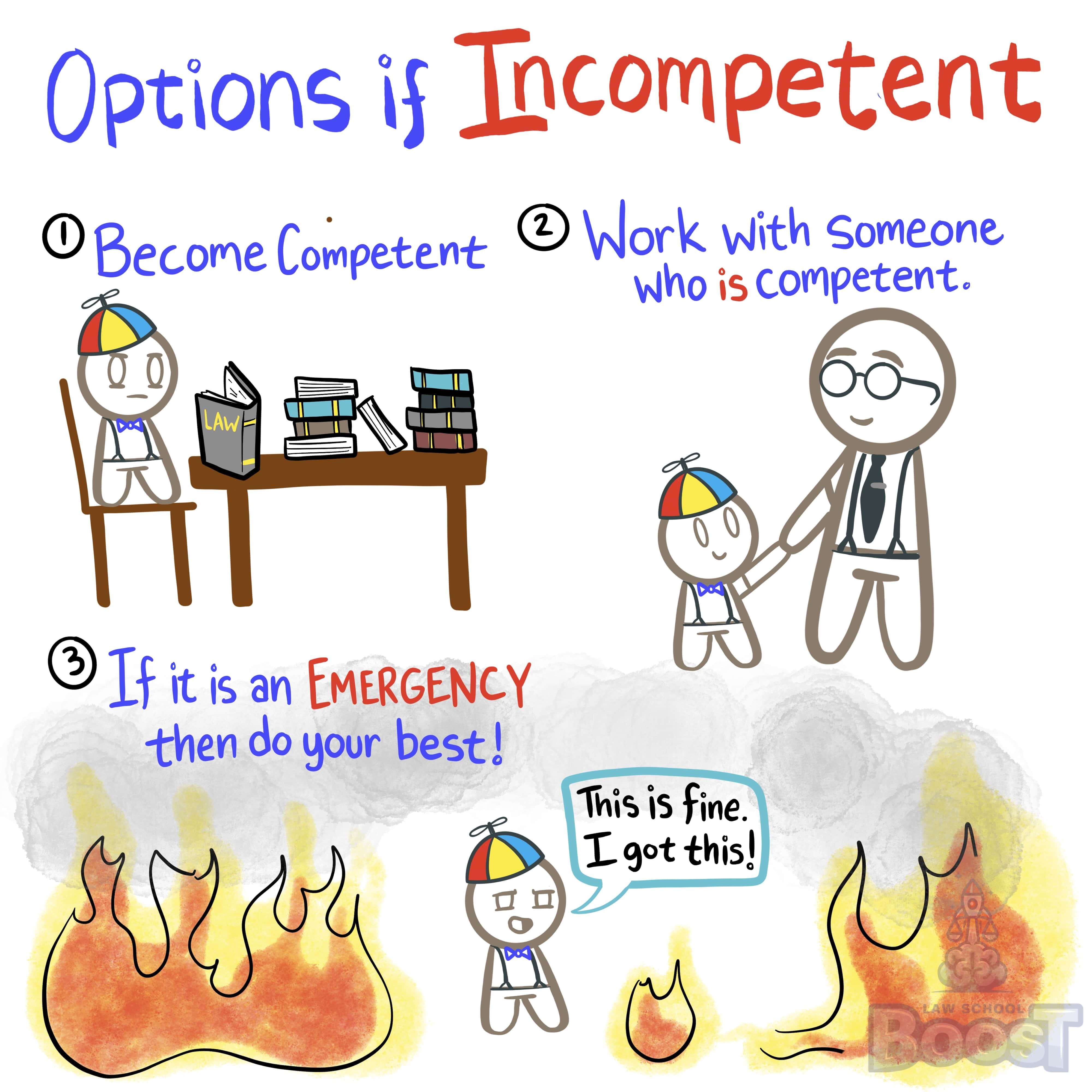
The duty of competence requires an attorney to have the knowledge, skill, preparation and thoroughness necessary to undertake effective representation of the client. If the lawyer does not possess these abilities, they can still undertake representation if: (1) they can learn the necessary knowledge within a reasonable time that does not cause the client undue delay; (2) they associate and work with an experienced attorney; or (3) face an emergency situation.
Plain English Explanation
Imagine you're about to have surgery. You'd expect your surgeon to know exactly what they're doing, right? The same principle applies to lawyers. When you hire a lawyer, you're trusting them with important matters that can significantly impact your life, finances, or freedom. That's why the duty of competence is so crucial in the legal profession... because dumb/incompetent attorneys can cause a lot of harm.
At its core, this rule is about protecting clients. It ensures that lawyers don't take on cases they can't handle effectively. But it's not just about book smarts or courtroom skills. The duty of competence covers a broad spectrum: knowledge of the law, practical skills in applying it, thorough preparation for each case, and the ability to be comprehensive in addressing all aspects of a legal matter.
However, the legal world is vast and complex. No lawyer can be an expert in every area of law. That's why the rule provides some flexibility. If a lawyer doesn't have the necessary expertise, they have a few options:
(1) They can learn. This isn't about starting from scratch – it's more like a doctor reading up on the latest treatment for a condition they don't see often. The key is that this learning process shouldn't cause undue delay for the client. It's a balancing act between expanding knowledge and serving the client promptly.
(2) Lawyers can team up. This is like a general practitioner bringing in a specialist for a complex medical case. By associating with an experienced attorney, a less experienced lawyer can take on more challenging cases while ensuring the client gets top-notch representation.
(3) There's an emergency exception. This recognizes that sometimes, immediate action is necessary even if the ideal expert isn't available. It's similar to how a doctor might need to provide emergency care outside their specialty if no one else is available.
The duty of competence doesn't mean a lawyer needs to be perfect or all-knowing. It means they need to be honest about their capabilities and take responsible steps to ensure their clients receive skilled representation. This rule helps maintain the integrity of the legal profession and protects clients from incompetent representation that could harm their interests.
At its core, this rule is about protecting clients. It ensures that lawyers don't take on cases they can't handle effectively. But it's not just about book smarts or courtroom skills. The duty of competence covers a broad spectrum: knowledge of the law, practical skills in applying it, thorough preparation for each case, and the ability to be comprehensive in addressing all aspects of a legal matter.
However, the legal world is vast and complex. No lawyer can be an expert in every area of law. That's why the rule provides some flexibility. If a lawyer doesn't have the necessary expertise, they have a few options:
(1) They can learn. This isn't about starting from scratch – it's more like a doctor reading up on the latest treatment for a condition they don't see often. The key is that this learning process shouldn't cause undue delay for the client. It's a balancing act between expanding knowledge and serving the client promptly.
(2) Lawyers can team up. This is like a general practitioner bringing in a specialist for a complex medical case. By associating with an experienced attorney, a less experienced lawyer can take on more challenging cases while ensuring the client gets top-notch representation.
(3) There's an emergency exception. This recognizes that sometimes, immediate action is necessary even if the ideal expert isn't available. It's similar to how a doctor might need to provide emergency care outside their specialty if no one else is available.
The duty of competence doesn't mean a lawyer needs to be perfect or all-knowing. It means they need to be honest about their capabilities and take responsible steps to ensure their clients receive skilled representation. This rule helps maintain the integrity of the legal profession and protects clients from incompetent representation that could harm their interests.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Bob, a corporate lawyer, agrees to represent Sam in a complex medical malpractice case, despite having no experience in this area. Bob doesn't research medical malpractice law or consult with experienced attorneys, believing he can figure it out as he goes along. Result: Bob has violated the duty of competence. He lacks the necessary knowledge and skills for medical malpractice cases and isn't taking appropriate steps to gain competence or associate with an experienced attorney.
Hypo 2: Bob, a general practitioner, is approached by Sam for help with a straightforward will. Bob has never drafted a will before but spends a week studying estate planning law and consulting with a mentor. He then feels confident he can competently draft Sam's will. Result: Bob has likely complied with the duty of competence. He recognized his lack of experience, took reasonable steps to gain the necessary knowledge within a reasonable time, and the delay likely didn't harm the client.
Hypo 3: Bob, a criminal defense lawyer, is asked by Sam to handle a complex tax fraud case. Recognizing his lack of expertise in tax law, Bob associates with Tim, an experienced tax attorney, to work on the case together. Result: Bob has complied with the duty of competence. By associating with an experienced tax attorney, Bob ensures that Sam receives competent representation in this complex matter.
Hypo 4: Bob, a family law attorney, receives an emergency call from Sam, who needs immediate help with a restraining order. Despite having no experience with restraining orders, Bob agrees to help because of the urgent nature of the situation. Result: Bob's actions likely comply with the duty of competence under the emergency exception. The immediate need for assistance justifies Bob taking on a matter outside his usual area of practice. Note that this would also trigger ethical issues related to fee splitting, which is covered in other cards.
Hypo 2: Bob, a general practitioner, is approached by Sam for help with a straightforward will. Bob has never drafted a will before but spends a week studying estate planning law and consulting with a mentor. He then feels confident he can competently draft Sam's will. Result: Bob has likely complied with the duty of competence. He recognized his lack of experience, took reasonable steps to gain the necessary knowledge within a reasonable time, and the delay likely didn't harm the client.
Hypo 3: Bob, a criminal defense lawyer, is asked by Sam to handle a complex tax fraud case. Recognizing his lack of expertise in tax law, Bob associates with Tim, an experienced tax attorney, to work on the case together. Result: Bob has complied with the duty of competence. By associating with an experienced tax attorney, Bob ensures that Sam receives competent representation in this complex matter.
Hypo 4: Bob, a family law attorney, receives an emergency call from Sam, who needs immediate help with a restraining order. Despite having no experience with restraining orders, Bob agrees to help because of the urgent nature of the situation. Result: Bob's actions likely comply with the duty of competence under the emergency exception. The immediate need for assistance justifies Bob taking on a matter outside his usual area of practice. Note that this would also trigger ethical issues related to fee splitting, which is covered in other cards.
Visual Aids