🏥
Remedies • Tort - Equitable Remedies
REM#030
Legal Definition
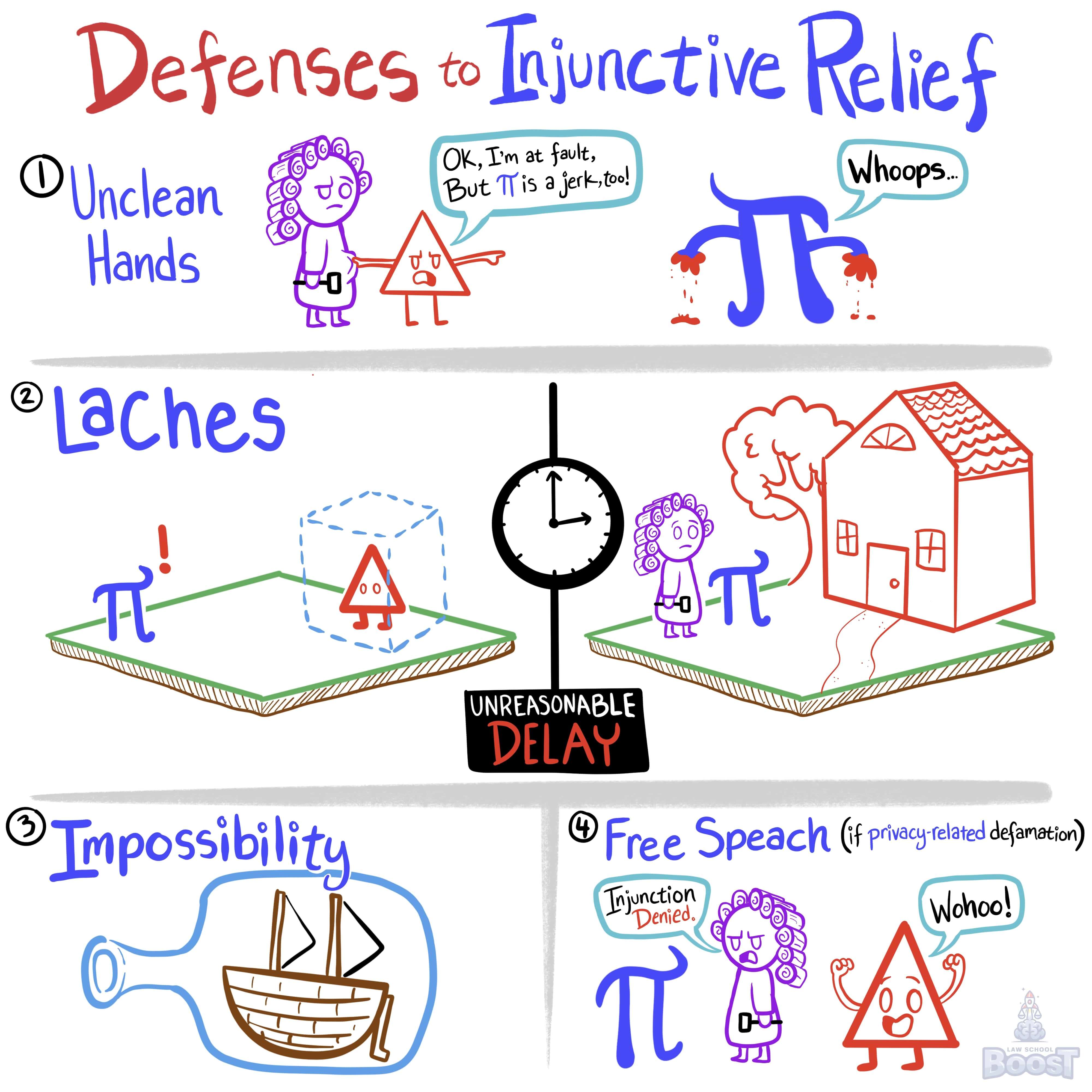
The defenses to injunctive relief are: (1) unclean hands ; (2) laches; (3) impossibility; and (4) free speech.
Plain English Explanation
When someone asks the court to stop you from doing something (called "injunctive relief"), you can defend yourself by saying:
(1) "They did something wrong too!" (unclean hands)
(2) "They waited too long to complain!" (laches)
(3) "It's impossible for me to do what they're asking!" (impossibility)
(4) "I have the right to speak freely!" (free speech)
(1) "They did something wrong too!" (unclean hands)
(2) "They waited too long to complain!" (laches)
(3) "It's impossible for me to do what they're asking!" (impossibility)
(4) "I have the right to speak freely!" (free speech)
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Bob plays loud music every night. Sam asks the court to make Bob stop. Bob says that Sam also plays loud music sometimes. Result: Bob uses the "unclean hands" defense, saying Sam did something wrong too. The court might consider this before deciding.
Hypo 2: Bob has been painting his house a bright pink color for years. Sam suddenly asks the court to make Bob change the color. Bob says Sam waited too long to complain. Result: Bob uses the "laches" defense, saying Sam took too long. The court might not make Bob change the color.
Hypo 3: Bob writes a blog post criticizing a new movie. Sam, the movie's director, asks the court to make Bob remove the post. Bob says he has the right to his opinion. Result: Bob uses the "free speech" defense. The court likely won't make Bob remove the post.
Hypo 4: Bob owns a very large parcel of land. Bob never mowed his lawn, and it became a jungle. Sam didn't say anything for years. One day, Sam asks the court to make Bob mow his lawn daily because of how large it is and the cost to do so. Bob says it's impossible to mow daily. Result: Bob uses the "impossibility" defense. The court might ask Bob to mow regularly, but not daily.
Hypo 2: Bob has been painting his house a bright pink color for years. Sam suddenly asks the court to make Bob change the color. Bob says Sam waited too long to complain. Result: Bob uses the "laches" defense, saying Sam took too long. The court might not make Bob change the color.
Hypo 3: Bob writes a blog post criticizing a new movie. Sam, the movie's director, asks the court to make Bob remove the post. Bob says he has the right to his opinion. Result: Bob uses the "free speech" defense. The court likely won't make Bob remove the post.
Hypo 4: Bob owns a very large parcel of land. Bob never mowed his lawn, and it became a jungle. Sam didn't say anything for years. One day, Sam asks the court to make Bob mow his lawn daily because of how large it is and the cost to do so. Bob says it's impossible to mow daily. Result: Bob uses the "impossibility" defense. The court might ask Bob to mow regularly, but not daily.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
What are equitable remedies in tort?
What is a preliminary injunction and how is it issued?
What is a temporary restraining order ("TRO") and what is required to get one?
What is contempt?
What is the collateral bar rule?
What parties are bound by an injunction?
When assessing a permanent injunction, how do courts balance hardships?
When assessing defenses to a lawsuit seeking injunctive relief, when are unclean hands applicable?
When assessing defenses to a lawsuit seeking injunctive relief, when is impossibility applicable?
When assessing defenses to a lawsuit seeking injunctive relief, when is laches applicable?
When deciding on a permanent injunction, when may ejectment be inadequate?
When deciding on applying a permanent injunction, when may money damages be inadequate?
When may replevin be inadequate as a remedy and, instead, a court will opt for a permanent injunction?
When will a court issue a permanent injunction?


