👀
Torts • Defenses to Intentional Torts
TORT#012
Legal Definition
Express consent is not valid in 3 situations: (1) where there was a mistake the defendant knew about, (2) where consent was induced by fraud regarding an essential matter, or (3) consent obtained via duress.
Plain English Explanation
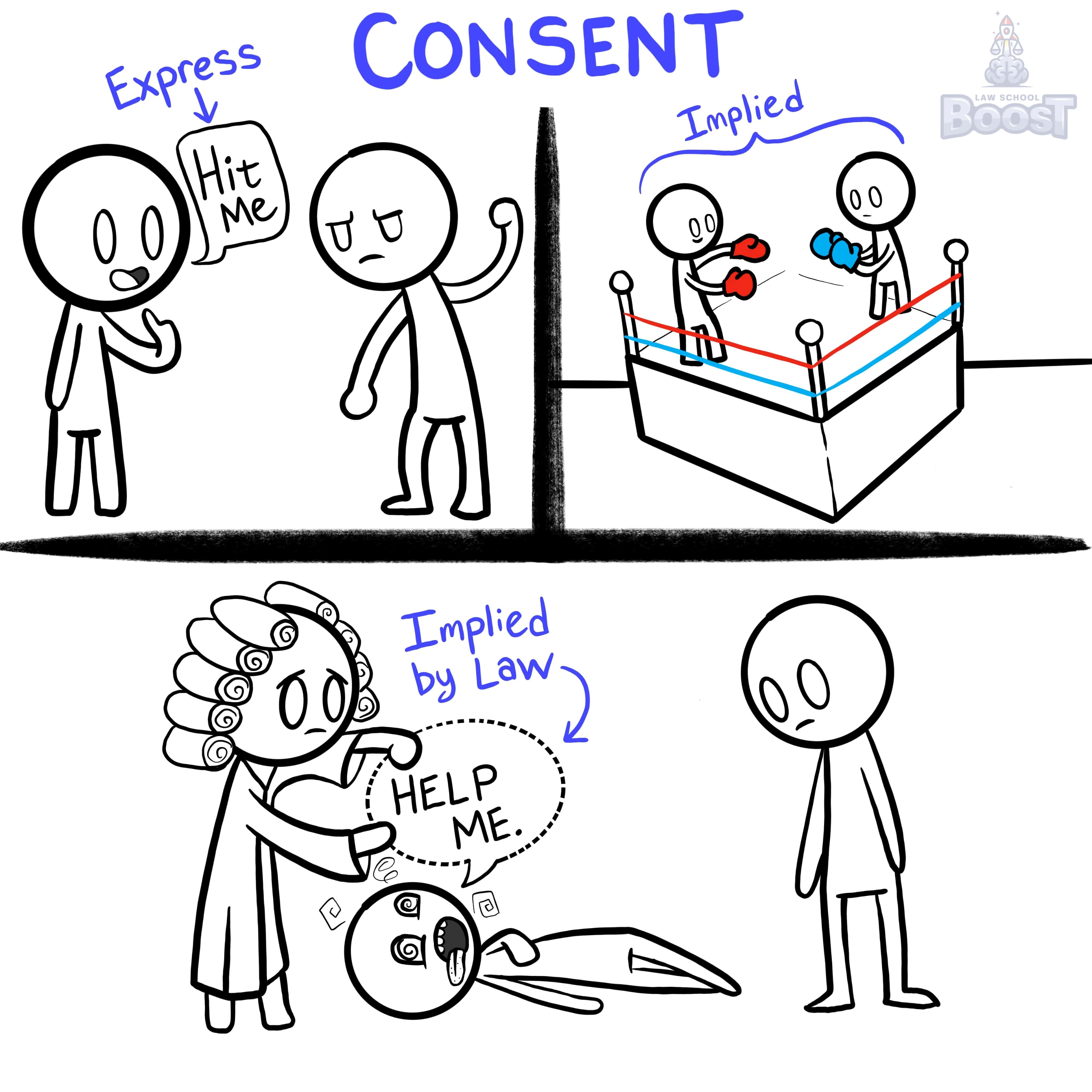
Express consent is consent that is clear, direct, and obvious. It's the kind of consent you agree to on a waiver when you go to the gym — the super specific kind where everyone should understand what is being consented to without having to guess or infer. Express consent requires a certain amount of trust and good-faith between the parties. Where one party obtains express consent by being dishonest, or even taking advantage of the person giving consent, the consent isn't valid. Express consent should be pure, in that the person giving it is aware of the consequences of their consent to the same extent as the party receiving consent.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Sam has two cars: a super fancy red sports car, and an old rusted minivan. Bob really wants to drive Sam's sports car, but Sam has made it clear on numerous occasions that Bob may not, however, he is always welcome to borrow the minivan. One day, Bob comes over and asks if he can borrow Sam's vehicle. Sam says, "Sure, the keys are on the table." Bob grabs the keys, walks out front, and realizes that the keys are to the fancy red sports car, not the minivan. Bob hops in the sports car and drives off. Later, when Sam sues Bob for trespass to chattel, Bob says that was given express consent to take the keys to the sports car. Result: Obviously, based on the situation, Sam made a mistake in which keys he told Bob to use. Bob realized the mistake, and still took advantage.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
In assessing a tort against property, what is a private necessity?
In assessing a tort against property, what is a public necessity?
In assessing a tort against property, what is necessity?
What is consent and its limitations?
What is the shopkeeper's privilege?
When is consent implied?
When is consent implied by law?
When is defense of others proper?
When is defense of property proper?
When is self-defense proper?
When may an actor recapture a chattel?


