🥺
Trusts • Modification and Termination of Trusts
TRUSTS#029
Legal Definition
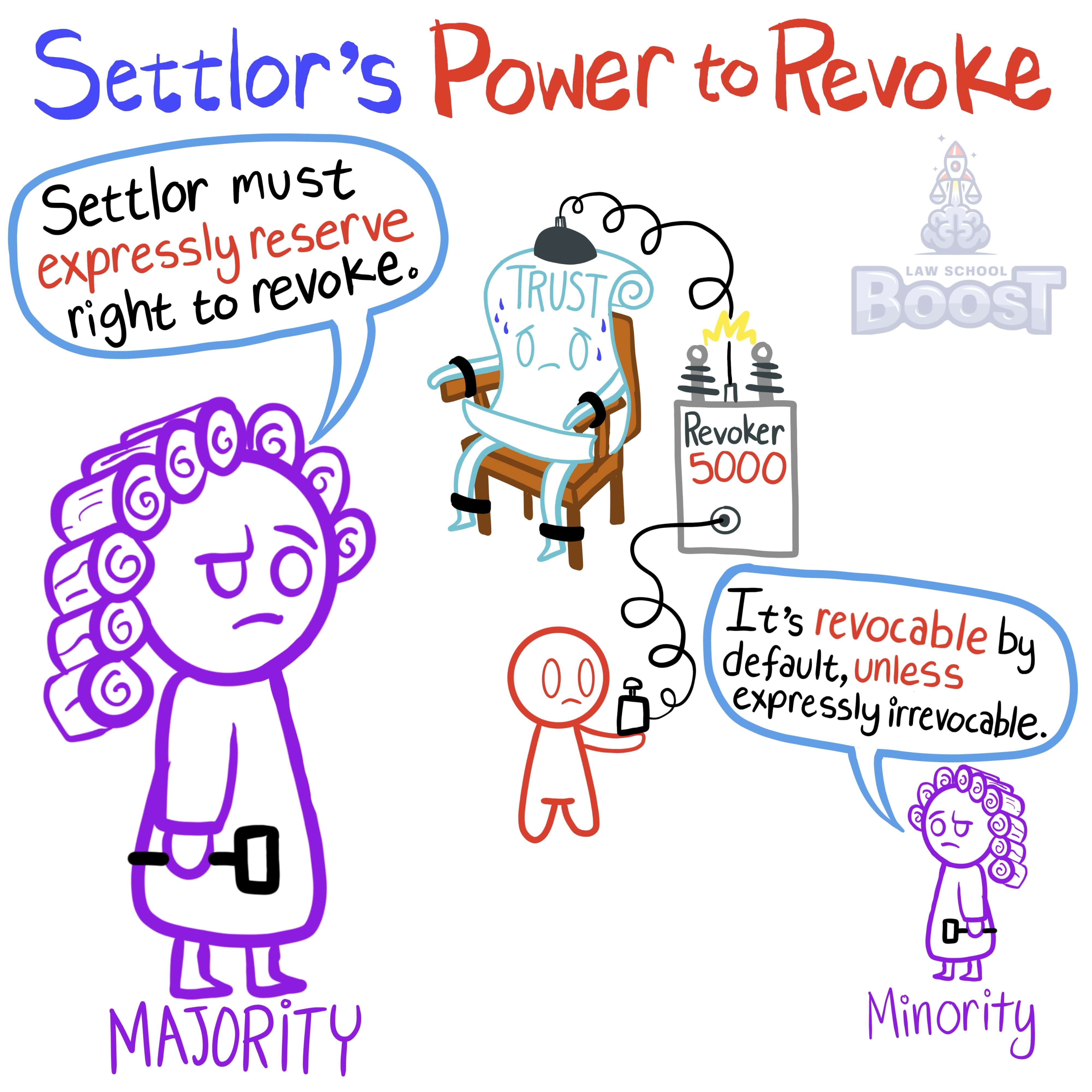
Under the majority view, in order to retain the power to revoke, the settlor must expressly reserve the power in the trust instrument. Under the minority view, the settlor retains the power to revoke unless the trust is made expressly irrevocable.
Plain English Explanation
Sometimes people create trusts and then later decide they want to terminate or "revoke" the trust. Whether or not they can do so depends on other facts and what jurisdiction they are in.
In most jurisdictions, in order to revoke a trust, its creator must have expressly put a term into the trust that reserves their right to do so. In other words, if a trust doesn't say something like "settlor reserves the right to revoke this trust," the creator has no right to later revoke the trust.
In a minority of jurisdictions, it is the opposite. In such jurisdictions, the creator of a trust will be presumed to have the right to later revoke the trust unless they expressly put a term into the trust that took away such a right by making the trust irrevocable.
In most jurisdictions, in order to revoke a trust, its creator must have expressly put a term into the trust that reserves their right to do so. In other words, if a trust doesn't say something like "settlor reserves the right to revoke this trust," the creator has no right to later revoke the trust.
In a minority of jurisdictions, it is the opposite. In such jurisdictions, the creator of a trust will be presumed to have the right to later revoke the trust unless they expressly put a term into the trust that took away such a right by making the trust irrevocable.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Sam creates a trust to manage his wealth and mentions in the document that he can cancel the trust whenever he wants. After a few years, he decides to revoke the trust. Result: Since Sam clearly stated in the trust that he can revoke it, under the majority view, he legally has the right to cancel it.
Hypo 2: Bob sets up a trust for his children but doesn't mention anything about revoking it. A couple of years later, he changes his mind and wants to cancel the trust. Result: Since Bob didn't expressly reserve the right to revoke the trust, under the majority view, he cannot legally cancel it. However, under the minority view, because Bob didn't say it was irrevocable, the courts would allow him to revoke the trust.
Hypo 3: Sam, living in a jurisdiction following the minority view, creates a trust without stating whether it's revocable or not. Later, he decides to revoke the trust. Result: In this minority jurisdiction, since Sam didn’t specifically make the trust irrevocable, he retains the right to revoke it.
Hypo 4: Sam creates a will, not a trust, leaving his property to his children. Years later, he decides to change the beneficiaries. Result: The rule about revoking trusts does not apply here because Sam’s document is a will, not a trust. He can change his will as it is a separate legal document with different rules.
Hypo 2: Bob sets up a trust for his children but doesn't mention anything about revoking it. A couple of years later, he changes his mind and wants to cancel the trust. Result: Since Bob didn't expressly reserve the right to revoke the trust, under the majority view, he cannot legally cancel it. However, under the minority view, because Bob didn't say it was irrevocable, the courts would allow him to revoke the trust.
Hypo 3: Sam, living in a jurisdiction following the minority view, creates a trust without stating whether it's revocable or not. Later, he decides to revoke the trust. Result: In this minority jurisdiction, since Sam didn’t specifically make the trust irrevocable, he retains the right to revoke it.
Hypo 4: Sam creates a will, not a trust, leaving his property to his children. Years later, he decides to change the beneficiaries. Result: The rule about revoking trusts does not apply here because Sam’s document is a will, not a trust. He can change his will as it is a separate legal document with different rules.
Visual Aids