😭
Wills • Revocation
WILLS#024
Legal Definition
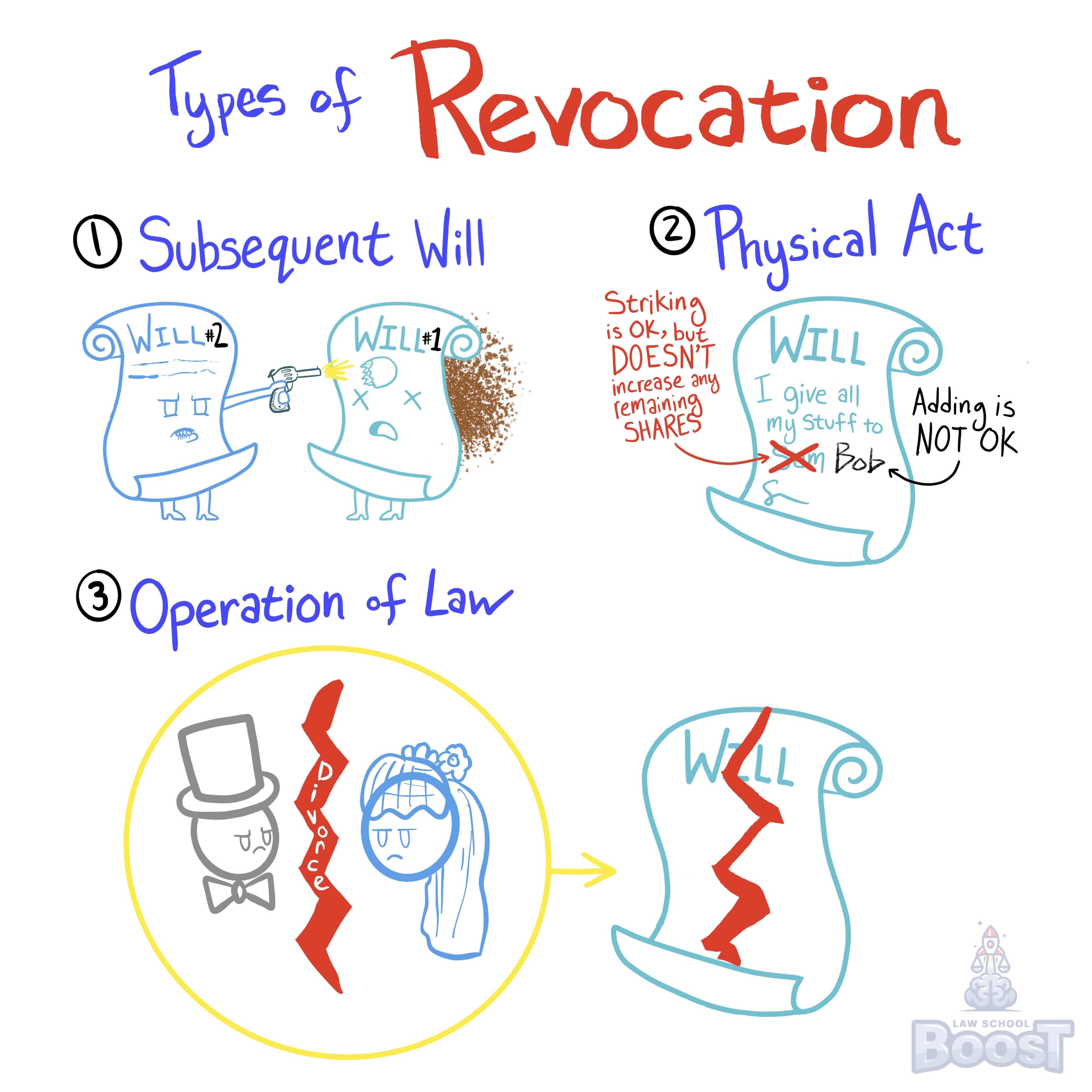
There are three methods of revocation: (1) by subsequent will (either expressly or impliedly), where Will #2 disposes of the entire estate; (2) by physical act (cancellation, tearing, blotting out, etc.) with simultaneous intent to revoke, either accomplished by the testator or someone at their direction; or (3) by operation of law (e.g., divorce, or termination of domestic partnership).
Plain English Explanation
A will that someone chooses today isn't necessarily the will that they will want to use when they die. It is common for wills that were, at one time, wanted to be revoked at a later point. There are three ways to revoke a will, or a part of a will:
(1) One obvious way to revoke a will is to create a new will that either expressly revokes the old one (by saying something like, "This will supersedes and revokes previous wills," or impliedly revokes the old one by simply covering the same stuff that it did (i.e., if the old will gives the testator's house to Bob, and the new one gives the same house to Sam, its implied that the new will revokes the old one since now Sam gets the house instead of Bob).
(2) Another pretty obvious way to revoke a will (or part of it) is through a physical act. For example, tearing up a will is a pretty good way to signify "I don't like this anymore. It is revoked." Similarly, if a will says "Bob gets my house," but later the testator scribbles that part out and notes the update, then its obvious that intent has changed and Bob should no longer get the house.
(3) Finally, sometimes the law steps in and revokes wills for the sake of public policy. For example, in some states, when spouses divorce, the law assumes that if they no longer love each other enough to stay married, they probably don't want to give each other things in their wills, which means their wills (or certain provisions) get revoked automatically.
(1) One obvious way to revoke a will is to create a new will that either expressly revokes the old one (by saying something like, "This will supersedes and revokes previous wills," or impliedly revokes the old one by simply covering the same stuff that it did (i.e., if the old will gives the testator's house to Bob, and the new one gives the same house to Sam, its implied that the new will revokes the old one since now Sam gets the house instead of Bob).
(2) Another pretty obvious way to revoke a will (or part of it) is through a physical act. For example, tearing up a will is a pretty good way to signify "I don't like this anymore. It is revoked." Similarly, if a will says "Bob gets my house," but later the testator scribbles that part out and notes the update, then its obvious that intent has changed and Bob should no longer get the house.
(3) Finally, sometimes the law steps in and revokes wills for the sake of public policy. For example, in some states, when spouses divorce, the law assumes that if they no longer love each other enough to stay married, they probably don't want to give each other things in their wills, which means their wills (or certain provisions) get revoked automatically.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Bob writes a will leaving his antique car collection to Sam. Later, he writes another will leaving his entire estate, including the cars, to his nephew. Result: Bob's second will impliedly revokes the first one because his more updated will also includes the cars. Thus, Sam won't get the cars because it is clear Bob changed his mind to give them to his nephew instead.
Hypo 2: Bob writes a will giving his house to Sam. Years later, angry with Sam, Bob crosses out Sam's name on the will and writes "VOID" across it. Result: Since Bob physically altered the will with the intention to revoke it, Sam no longer inherits the house.
Hypo 3: Bob writes a will giving his guitar collection to Sam. Later, thinking of changing his will, Bob discusses his plans with a friend but doesn't take any action. Result: Since Bob didn't make a new will or physically alter the existing one, Sam still inherits the guitars.
Hypo 4: Bob promises Sam a watch but never includes it in a will. After a falling out, Bob decides not to give Sam the watch. Result: Since the watch was never part of a will, the rule about revoking gifts in a will doesn't apply here. This is just a broken personal promise, not a legal issue under this rule.
Hypo 2: Bob writes a will giving his house to Sam. Years later, angry with Sam, Bob crosses out Sam's name on the will and writes "VOID" across it. Result: Since Bob physically altered the will with the intention to revoke it, Sam no longer inherits the house.
Hypo 3: Bob writes a will giving his guitar collection to Sam. Later, thinking of changing his will, Bob discusses his plans with a friend but doesn't take any action. Result: Since Bob didn't make a new will or physically alter the existing one, Sam still inherits the guitars.
Hypo 4: Bob promises Sam a watch but never includes it in a will. After a falling out, Bob decides not to give Sam the watch. Result: Since the watch was never part of a will, the rule about revoking gifts in a will doesn't apply here. This is just a broken personal promise, not a legal issue under this rule.
Visual Aids