🇺🇸
Constitutional Law • First Amendment - Free Speech
CONLAW#120
Legal Definition
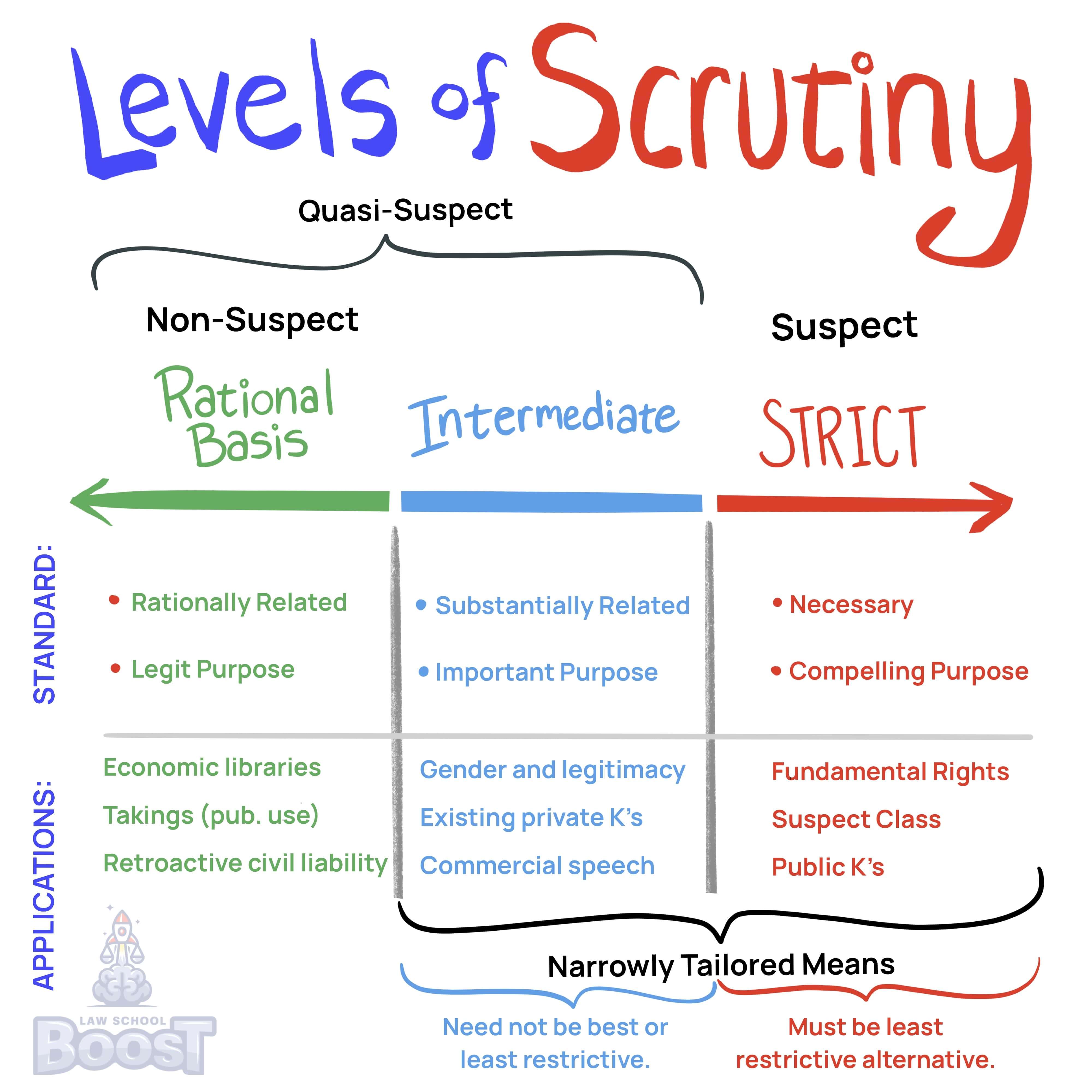
According to *Chemerinsky*, court orders suppressing speech must meet strict scrutiny, although a procedurally proper court order must be complied with until vacated or overturned. One violating a court order is collaterally barred from later challenging it. Gag orders on the press to prevent prejudicial pre-trial publicity are typically unconstitutional.
Plain English Explanation
Court orders that stop people from speaking must pass the strictest level of examination, known as "strict scrutiny." However, if a court order is issued properly, it must be followed until it is changed or overturned by a higher court. If you break such an order, you cannot argue against it later. Orders that stop the media from reporting to prevent unfair trials are generally not allowed.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
Are fighting words protected speech?
Are profane and indecent speech protected?
Can government speech be challenged?
How do you analyze a free speech issue?
Is anonymous speech protected?
Is discretion allowed in determining fees for public demonstrations?
Is speech protected when it incites illegal activity?
May the government seize assets of businesses that violate obscenity laws?
What are content-based restrictions, and which level of scrutiny is applied?
What are designated public forums?
What are limited public forums?
What are non-public forums?
What are prior restraints and when are they valid?
What are public forums?
What are the limits of free speech during a broadcast?
What does the 1st Amendment prohibit, and how is it applied?
What is the 1st Amendment right to access private property for speech?
What is the constitutionality of laws prohibiting group discrimination?
What level of scrutiny is applied to content-based restrictions on public forums?
What level of scrutiny is applied to laws impacting freedom of association?
What level of scrutiny is applied to laws that require disclosure of group membership?
What rights do the press have in addition to those granted to private citizens?
When are obscenities and sexually oriented speech considered obscene?
When are time, place, and manner restrictions on speech valid?
When is a law unconstitutionally overbroad?
When is a law unconstitutionally vague?
When is commercial speech protected, and when is it not?
When is speech by government employees not protected?
When may a private figure recover for defamation if there is no matter of public concern?
When may a private figure recover for defamation regarding a matter of public concern?
When may a public official or figure recover for defamation?
When may the government ban child pornography?
When may the government burden lawful, non-misleading, non-fraudulent commercial speech?
When may the government punish or limit news reporting?
When may the government punish private possession of obscene materials?
When may the government regulate symbolic speech?
When may the government require a license for speech?
When may the government use zoning ordinances to regulate adult businesses?
Which level of scrutiny is applied to content-neutral restrictions?


