‼️
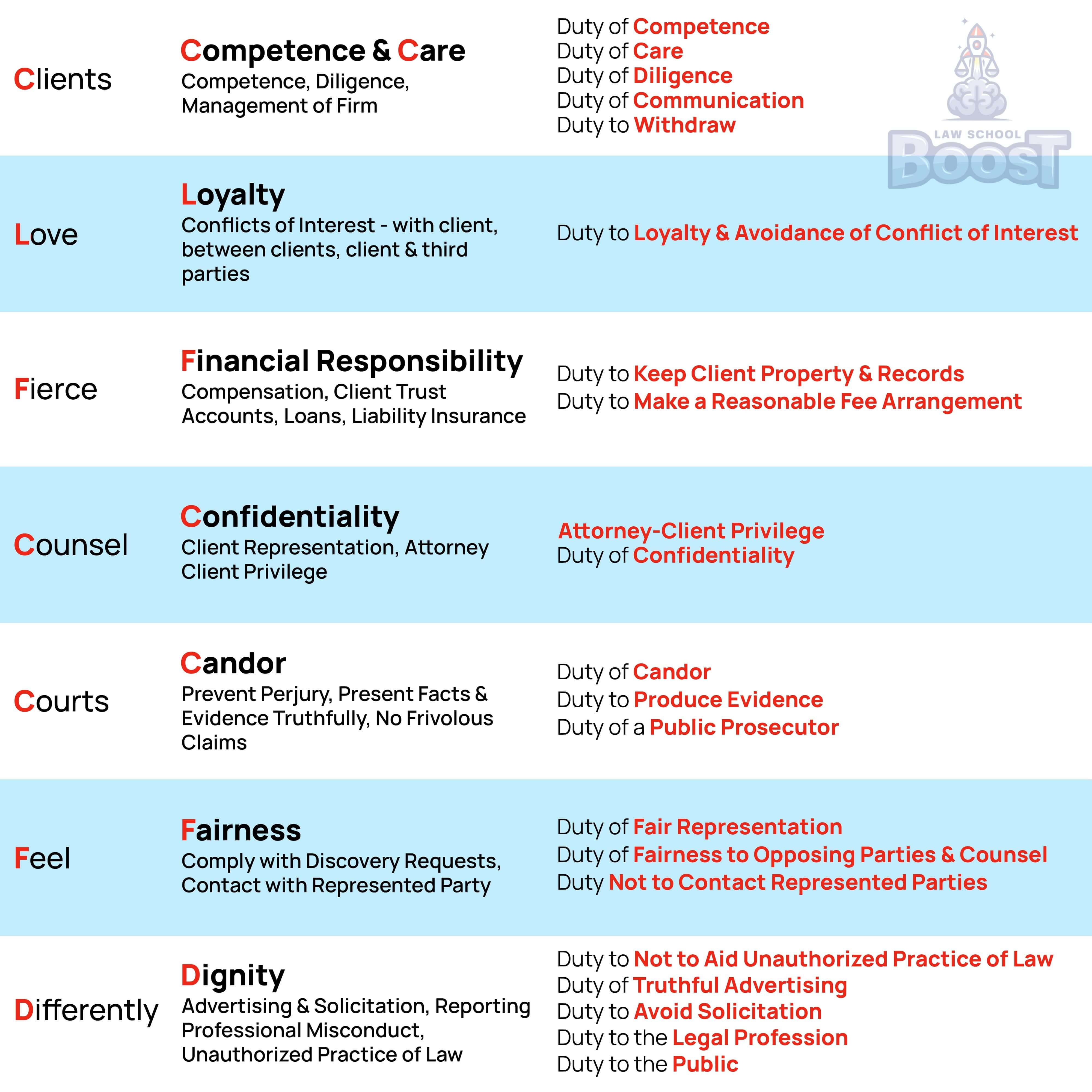
Prof Responsibility • Duty to Public
PR#083
Legal Definition
A lawyer has an independent duty to the public not to commit fraud, a crime, or any other serious immoral act.
Plain English Explanation
Lawyers have a special duty to the public to avoid bad behavior, even when they're not working on a case. This means they must not commit fraud, crimes, or do seriously wrong things. Let's break that down:
Fraud means intentionally tricking or deceiving someone, usually to get money or other benefits. For example, lying on official documents or pretending to be someone you're not to get their money would be fraud.
A crime is any action that breaks the law and can be punished by the government. This covers a wide range, from theft and assault to more complex white-collar crimes.
A serious immoral act refers to behavior that most people in society would consider very wrong or unethical, even if it's not technically illegal. This could include things like betraying a significant trust or cruelly taking advantage of vulnerable people.
Fraud means intentionally tricking or deceiving someone, usually to get money or other benefits. For example, lying on official documents or pretending to be someone you're not to get their money would be fraud.
A crime is any action that breaks the law and can be punished by the government. This covers a wide range, from theft and assault to more complex white-collar crimes.
A serious immoral act refers to behavior that most people in society would consider very wrong or unethical, even if it's not technically illegal. This could include things like betraying a significant trust or cruelly taking advantage of vulnerable people.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Bob is struggling financially in his solo law practice. A longtime client, Sam, approaches Bob with a scheme to defraud investors through a Ponzi scheme. Sam offers Bob a large cut of the profits if he helps create shell companies and draft fraudulent investment documents. Despite his financial troubles, Bob immediately refuses to participate and terminates his representation of Sam. Result: Bob acted ethically by refusing to participate in Sam's fraudulent scheme, even though it would have been financially lucrative. A lawyer's duty to avoid fraud and serious misconduct exists independently of client interests or the lawyer's own financial situation.
Hypo 2: Bob, frustrated with a difficult divorce case, accesses his ex-wife's email account using a password he remembers from their marriage. He reads through her recent emails, looking for information he can use in the divorce proceedings. Result: Bob has committed a crime by illegally accessing someone else's email account. This violates his duty as a lawyer to avoid criminal acts, even in his personal life. The fact that he's using his legal knowledge to gain an advantage in his own case makes this particularly problematic.
Hypo 3: Bob is struggling financially and "borrows" $10,000 from his client trust account, intending to replace it before anyone notices. He loses the money gambling and is unable to return it before a scheduled audit. Result: Bob has committed a serious breach of ethics and likely a crime by misappropriating client funds. This is a clear violation of his duty to avoid fraud and criminal acts. The fact that he intended to return the money doesn't excuse the action.
Hypo 4: Bob, driving home after a few drinks at a bar, is pulled over by police. He flashes his bar card and tries to talk his way out of a sobriety test, implying he has connections in the local court. Result: Bob's actions, while not necessarily criminal, constitute a serious immoral act. He's attempting to use his position as a lawyer to evade the law, which violates his duty to uphold the integrity of the legal profession. Additionally, driving under the influence is a crime, further violating his ethical obligations.
Hypo 2: Bob, frustrated with a difficult divorce case, accesses his ex-wife's email account using a password he remembers from their marriage. He reads through her recent emails, looking for information he can use in the divorce proceedings. Result: Bob has committed a crime by illegally accessing someone else's email account. This violates his duty as a lawyer to avoid criminal acts, even in his personal life. The fact that he's using his legal knowledge to gain an advantage in his own case makes this particularly problematic.
Hypo 3: Bob is struggling financially and "borrows" $10,000 from his client trust account, intending to replace it before anyone notices. He loses the money gambling and is unable to return it before a scheduled audit. Result: Bob has committed a serious breach of ethics and likely a crime by misappropriating client funds. This is a clear violation of his duty to avoid fraud and criminal acts. The fact that he intended to return the money doesn't excuse the action.
Hypo 4: Bob, driving home after a few drinks at a bar, is pulled over by police. He flashes his bar card and tries to talk his way out of a sobriety test, implying he has connections in the local court. Result: Bob's actions, while not necessarily criminal, constitute a serious immoral act. He's attempting to use his position as a lawyer to evade the law, which violates his duty to uphold the integrity of the legal profession. Additionally, driving under the influence is a crime, further violating his ethical obligations.
Visual Aids