😀
Real Property • Future Interests
PROP#017
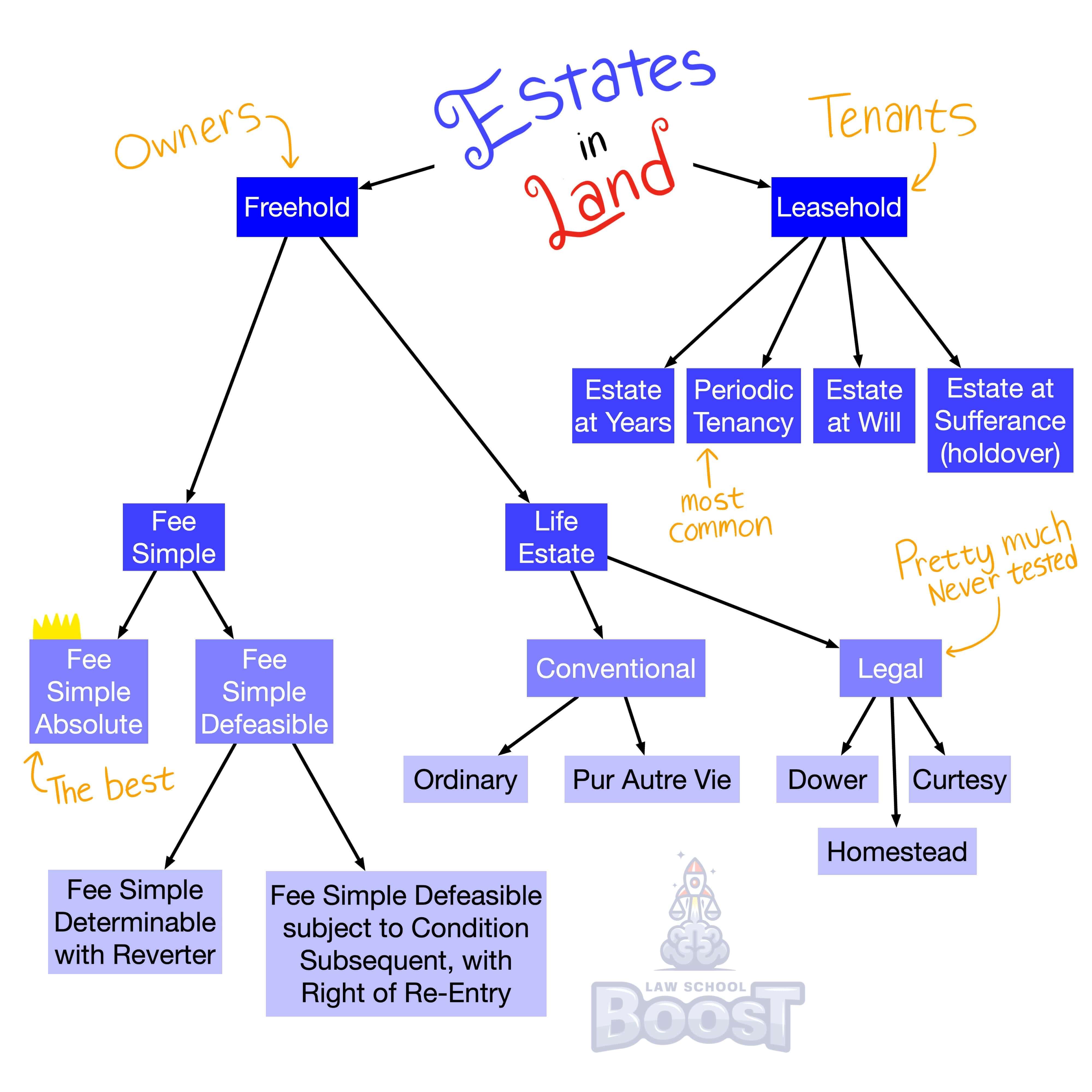
Legal Definition
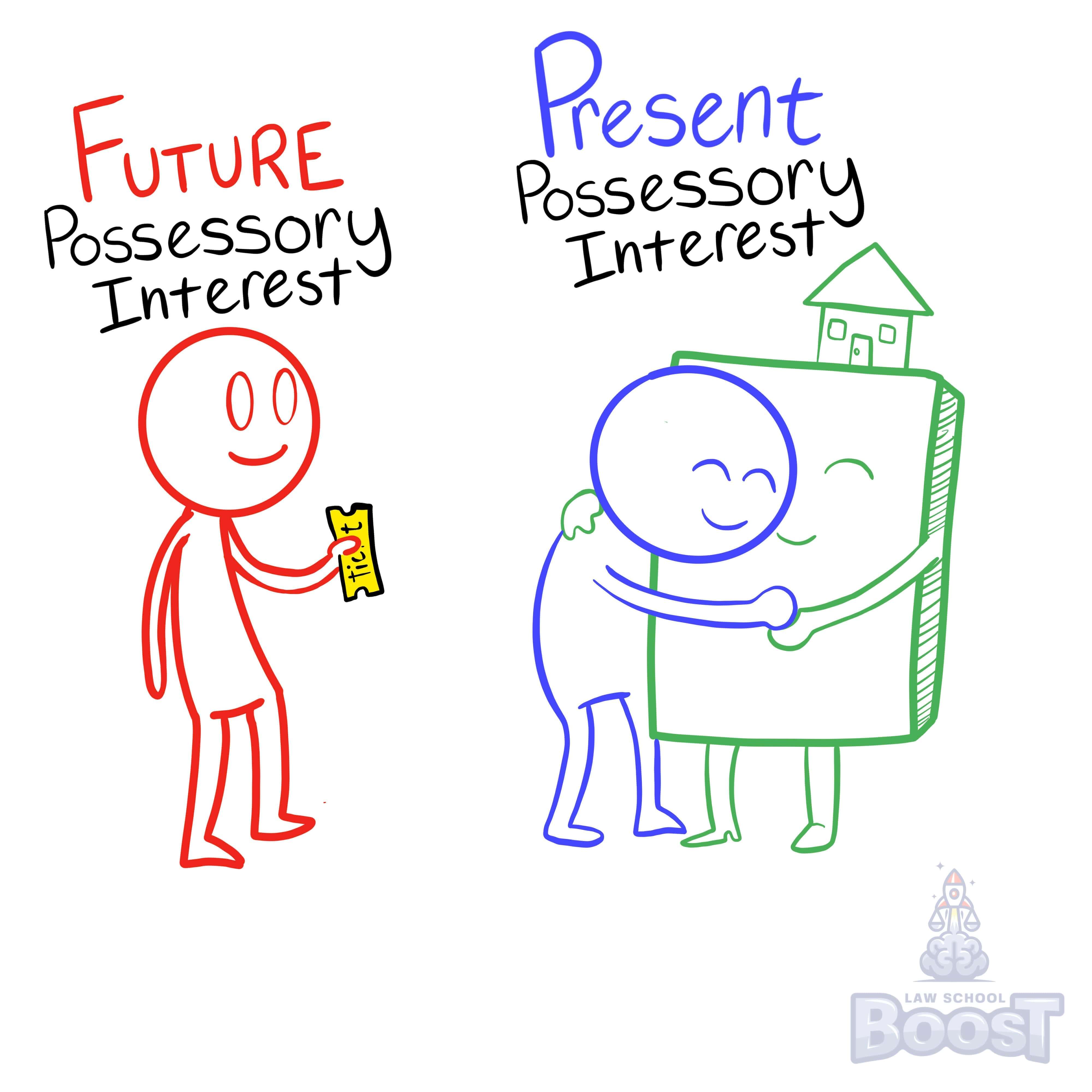
A future interest is a present, legally protected right in property that provides its holder with either the right or possibility of future possession of an estate.
Future interests in a grantor include a reversion, possibility of reverter, or right of entry, all of which are vested interests not subject to the Rule Against Perpetuities.
Future interests in a grantee include a vested or contingent remainder, springing executory interest, or shifting executive interest.
Future interests in a grantor include a reversion, possibility of reverter, or right of entry, all of which are vested interests not subject to the Rule Against Perpetuities.
Future interests in a grantee include a vested or contingent remainder, springing executory interest, or shifting executive interest.
Plain English Explanation
Most property law questions will require you to methodically break down a land conveyance in order to identify what specific interests each party has. "Future interests" are a class of many specific interests. When you've identified an interest as being a future interest, it means that even though the person doesn't have a present right to possess the land, their future interest is still presently protected under the law. In other words, they have the right to make sure whoever does presently possess the land doesn't cause harm to it, and present possessors owe future possessors certain duties.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Oz conveys Blackacre "to Amy for life, then to Bob." Result: Bob has no right to possess Blackacre while Amy is still alive, however, his future interest means that Amy owes him the duty to not commit waste with Blackacre. Additionally, Bob can sell his future interest in Blackacre to whoever he wants, or he can leave it to his heirs. His future interests may not come with any present possessory rights, but it comes with plenty of other present value.
Hypo 2: Oz conveys Blackacre "to Amy for life, then to Bob if Bob survives Amy." Result: Amy has a present possessory interest in Blackacre, called a life estate. Bob has a future interest in Blackacre, called a contingent remainder. In other words, Bob's future interest may become a present possessory interest in Blackacre if Amy dies before Bob. If Bob dies before Amy, Blackacre will go back to Oz because Oz has a future interest called a reversion.
Though this may all seem intimidating, property law has a lot of terminology you'll need to get familiar with in order to understand which rights are superior between parties.
Hypo 2: Oz conveys Blackacre "to Amy for life, then to Bob if Bob survives Amy." Result: Amy has a present possessory interest in Blackacre, called a life estate. Bob has a future interest in Blackacre, called a contingent remainder. In other words, Bob's future interest may become a present possessory interest in Blackacre if Amy dies before Bob. If Bob dies before Amy, Blackacre will go back to Oz because Oz has a future interest called a reversion.
Though this may all seem intimidating, property law has a lot of terminology you'll need to get familiar with in order to understand which rights are superior between parties.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
At common law, how was a contingent remainder destroyed?
In assessing a contingent remainder what is the doctrine of merger?
What is a class gift?
What is a contingent remainder?
What is an executory interest?
What is an indefeasibly vested remainder?
What is a remainder?
What is a shifting executory interest?
What is a springing executory interest?
What is a vested remainder subject to open?
What is a vested remainder subject to total divestment?
What is the Doctrine of Worthier Title?
What is the Rule in Shelley's Case?
What is the Rule of Convenience?


