😀
Real Property • Future Interests
PROP#031
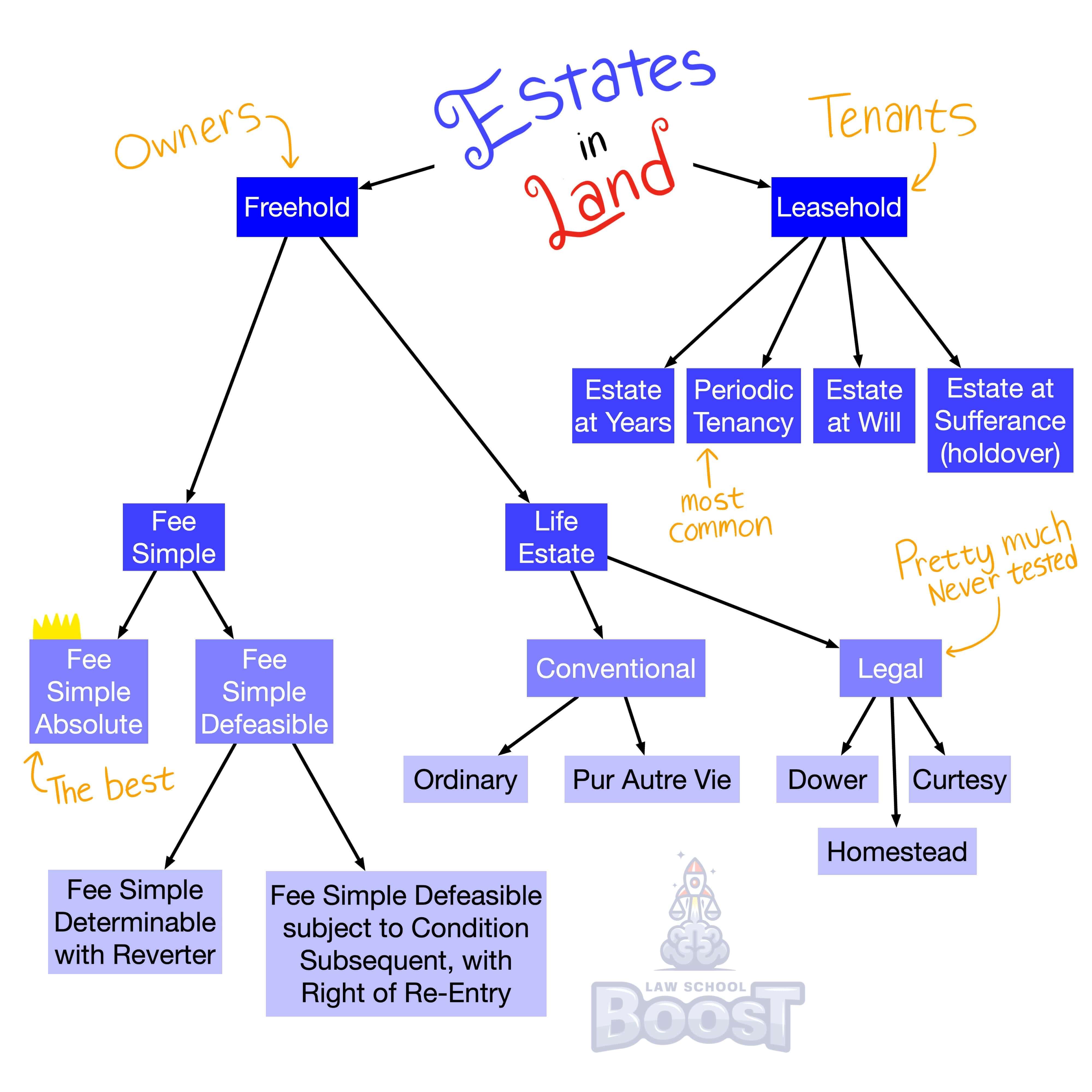
Legal Definition
Under the Rule of Convenience, a class closes when any member of the class can call for distribution of their share of the class gift.
Plain English Explanation
The problem with broad classes is that it is hard to know when they officially close. For example, if you convey Blackacre "to Amy's children," when do Amy's children actually get the interest in Blackacre? The most obvious answer is "when Amy dies." And yes, this is true. When Amy dies, Amy can definitively have no more children, so the class closes and all her children receive their share of Blackacre.
However, another option is the Rule of Convenience, which says that a class can be closed as soon as any member of the class is allowed to call for distribution. Let's jump over to Hypos for some examples.
However, another option is the Rule of Convenience, which says that a class can be closed as soon as any member of the class is allowed to call for distribution. Let's jump over to Hypos for some examples.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Oz conveys Blackacre "to Amy's children that pass the bar exam." Amy has 3 children: Bob, Carl, and Dan. Bob is the oldest and finishes law school first. While Carl begins law school, Bob passes the bar. Three years later, Carl graduates from law school and also passes the bar. Dan decides he also wants to go to law school. Carl demands a distribution of his share of Blackacre. Result: Blackacre will be divided between Bob and Carl, the only children of Amy who passed the bar exam. Sure, Dan wanted to also pass the bar exam, and he likely would have if he had time (especially if he used Bar Prep Buddy -- tell your friends!), but the Rule of Convenience allows any member of the class who is entitled to a share of the class gift to call for their distribution whenever they want. Here, Bob could have closed the class immediately when he passed the bar exam and owned 100% of Blackacre, but he didn't. Instead, Carl closed the class.
Hypo 2: Oz conveys Blackacre "to Amy for life, then to Bob's children." Bob has two children. Result: The class will definitively close when Bob dies and can no longer have children, but it can also close (under the Rule of Convenience) the moment Amy dies and either of Bob's children call for their distribution. This would effectively divide Blackacre between Bob's existing children and deprive any later children of a share. PLEASE NOTE: There is something called the "womb rule," which means a not-yet born fetus that existed at the time of the distribution would also be entitled to a share. So if Bob's wife is pregnant when one of his two born children call for a distribution, Blackacre would be divided 3-ways.
Hypo 2: Oz conveys Blackacre "to Amy for life, then to Bob's children." Bob has two children. Result: The class will definitively close when Bob dies and can no longer have children, but it can also close (under the Rule of Convenience) the moment Amy dies and either of Bob's children call for their distribution. This would effectively divide Blackacre between Bob's existing children and deprive any later children of a share. PLEASE NOTE: There is something called the "womb rule," which means a not-yet born fetus that existed at the time of the distribution would also be entitled to a share. So if Bob's wife is pregnant when one of his two born children call for a distribution, Blackacre would be divided 3-ways.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
At common law, how was a contingent remainder destroyed?
In assessing a contingent remainder what is the doctrine of merger?
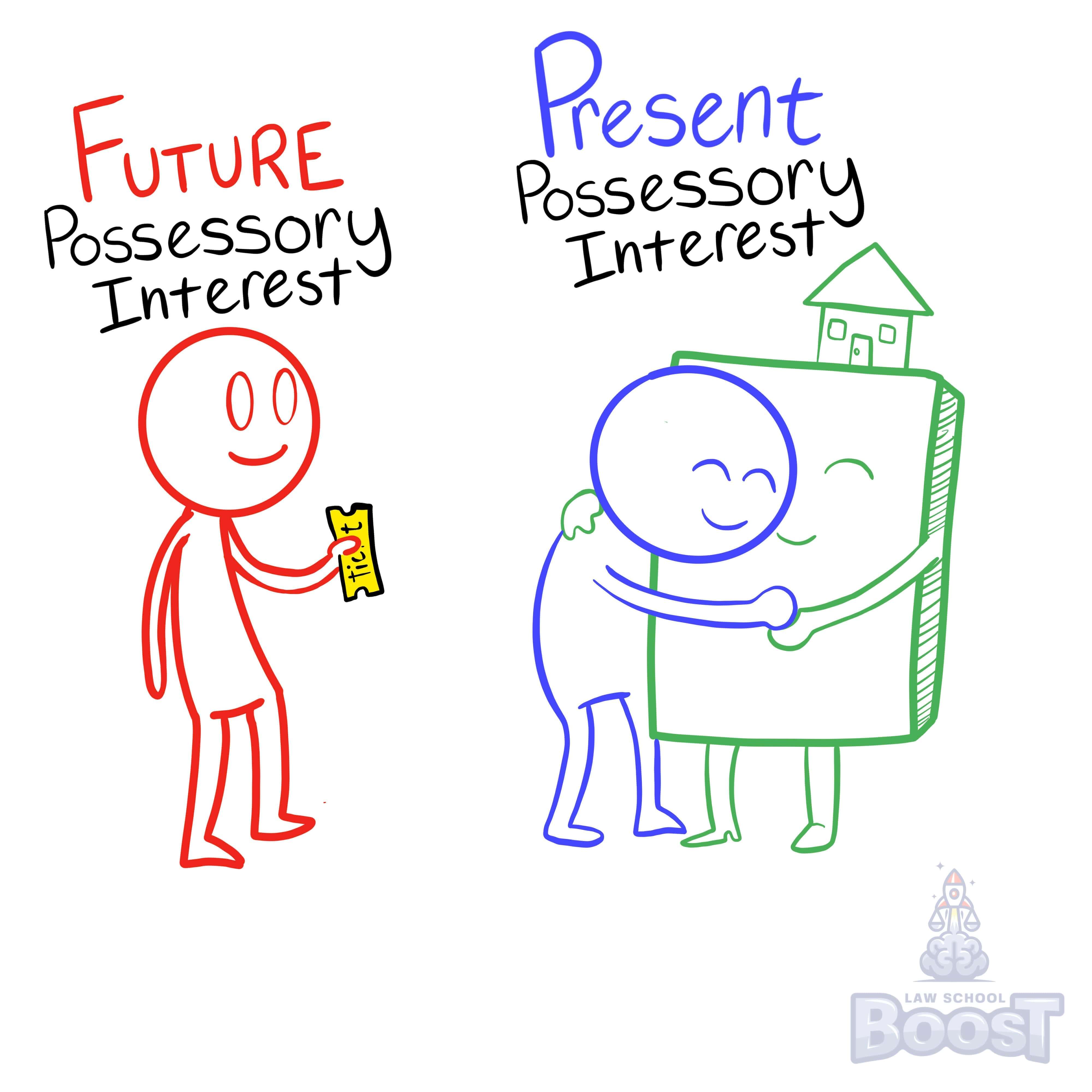
What are future interests?
What is a class gift?
What is a contingent remainder?
What is an executory interest?
What is an indefeasibly vested remainder?
What is a remainder?
What is a shifting executory interest?
What is a springing executory interest?
What is a vested remainder subject to open?
What is a vested remainder subject to total divestment?
What is the Doctrine of Worthier Title?
What is the Rule in Shelley's Case?


