😀
Real Property • Landlord-Tenant
PROP#065
Legal Definition
If a tenant remains in possession after their right has terminated, their landlord has the right to: (1) evict them, or (2) bind them to a new periodic tenancy under the same lease terms as before.
For commercial tenants, if the original lease term was 1 year or more, they may be held to a new year-to-year tenancy; if less than a year, then a periodic term based on rent payment frequency.
A holdover tenant will be found to have agreed to any rent increases if they were notified about them before the lease expired.
For commercial tenants, if the original lease term was 1 year or more, they may be held to a new year-to-year tenancy; if less than a year, then a periodic term based on rent payment frequency.
A holdover tenant will be found to have agreed to any rent increases if they were notified about them before the lease expired.
Plain English Explanation
The hold-over doctrine is a legal instruction manual for how to deal with tenants who stay longer than their original agreement allowed. Which options a landlord may choose from depends on what kind of tenant is holding-over.
First, the landlord always has the option to evict a holdover tenant. Eviction is a legal process where a landlord asks the court to assist removing someone who has no legal right to be on the property. This is true for residential and commercial tenants.
Second, the landlord can bind the tenant to a new periodic tenancy. For residential tenants, this will generally be month-to-month under the same terms as the original lease. For commercial tenants, it will depend on how long the tenant's previous term was for. If the previous term was for a year or more, then the landlord can bind them to another year-to-year tenancy. If it was less than a year, then the landlord can bind them to a tenancy for a period equal to whatever period was used for payment. For example, if a commercial tenant paid once per quarter, then the period would be quarter-to-quarter.
Note that when an agreement expires, it is an opportunity for a landlord to raise rent. If the landlord notifies the tenant of their intent to raise rent before the lease ends, then holding-over acts as acceptance to the higher rent, which the landlord can then demand be paid.
First, the landlord always has the option to evict a holdover tenant. Eviction is a legal process where a landlord asks the court to assist removing someone who has no legal right to be on the property. This is true for residential and commercial tenants.
Second, the landlord can bind the tenant to a new periodic tenancy. For residential tenants, this will generally be month-to-month under the same terms as the original lease. For commercial tenants, it will depend on how long the tenant's previous term was for. If the previous term was for a year or more, then the landlord can bind them to another year-to-year tenancy. If it was less than a year, then the landlord can bind them to a tenancy for a period equal to whatever period was used for payment. For example, if a commercial tenant paid once per quarter, then the period would be quarter-to-quarter.
Note that when an agreement expires, it is an opportunity for a landlord to raise rent. If the landlord notifies the tenant of their intent to raise rent before the lease ends, then holding-over acts as acceptance to the higher rent, which the landlord can then demand be paid.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Amy runs an ice cream parlor out of a space she rents from Bob. Amy signed a 1 year lease with Bob for $12,000 with payments of $1,000 due on the first of each month. 2 months before the end of the lease, Bob notifies Amy that he plans on raising rent to $20,000 the next year. During the last month of Amy's lease, Bob sends over the updated lease. Amy ignores it. Amy continues to stay in the building after her lease expires. Result: Amy had a periodic tenancy with Bob. The period was 1 year, and the rate was $12,000 per year paid in monthly installments. When Amy held-over after her lease expired, it created a new periodic tenancy with Bob for another year. Moreover, since Bob gave Amy notice that rent was going to increase, Amy now owes bob $20,000 in rent for the next year, paid in monthly installments. By holding-over and ignoring Bob's notice, Amy has agreed to the new lease and increase rent.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
How do lease covenants affect a landlord-tenant relationship where one party breaches?
How may a landlord waive a covenant prohibiting assignment?
If a leasehold is condemned or taken via eminent domain, what is the effect on a tenant's duty to pay rent?
If an assignment occurs, what is the relationship between the assignee and the landlord?
If a tenant breaches one or more of their duties, what remedies are available to the landlord?
If a tenant violates a covenant against assignment or sublease, what remedies are available to the landlord?
In a landlord-tenant relationship, who has a duty of restoration when the premises being leased are destroyed due to no fault of either party?
In assessing a landlord's tort liability, what six duties does a landlord have to make the premises safe?
In assessing a landlord-tenant issue, what is an assignment?
In assessing a landlord-tenant relationship, what are the landlord's duties?
In assessing a landlord-tenant relationship, what are the tenant's duties?
In assessing a landlord-tenant relationship, what is the result of a tenant's covenant to repair?
What are the exceptions to the hold-over doctrine?
What constitutes a constructive eviction?
What constitutes an actual eviction?
What constitutes a partial eviction?
What is a landlord's duty to deliver possession?
What is a landlord's duty to provide quiet enjoyment?
What is a landlord's duty to repair?
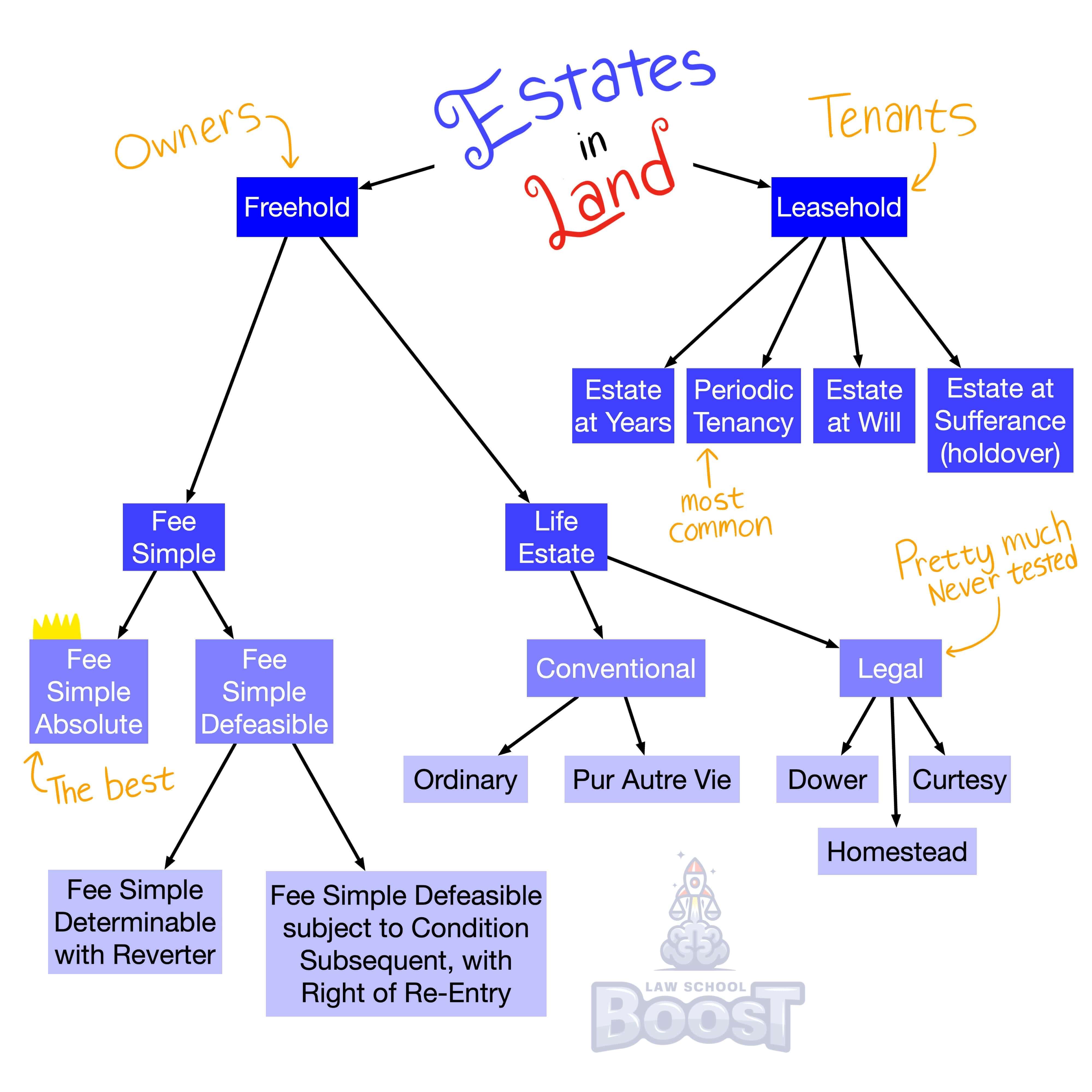
What is a leasehold estate?
What is a periodic tenancy and how does it terminate?
What is a retaliatory eviction?
What is a sublease?
What is a tenancy at sufferance and how does it terminate?
What is a tenancy at will and how does it terminate?
What is a tenancy for years and how does it terminate?
What is a tenant's duty to not use the premises for an illegal purpose?
What is a tenant's duty to pay rent, and how does it affect their security deposit?
What is a tenant's duty to repair?
What is the implied warranty of habitability, and what remedies are available to the tenant if breached?
When does a covenant run with the land?
When does a tenant cause ameliorative waste?
When does a tenant cause permissive waste?
When does a tenant cause voluntary waste?


