😀
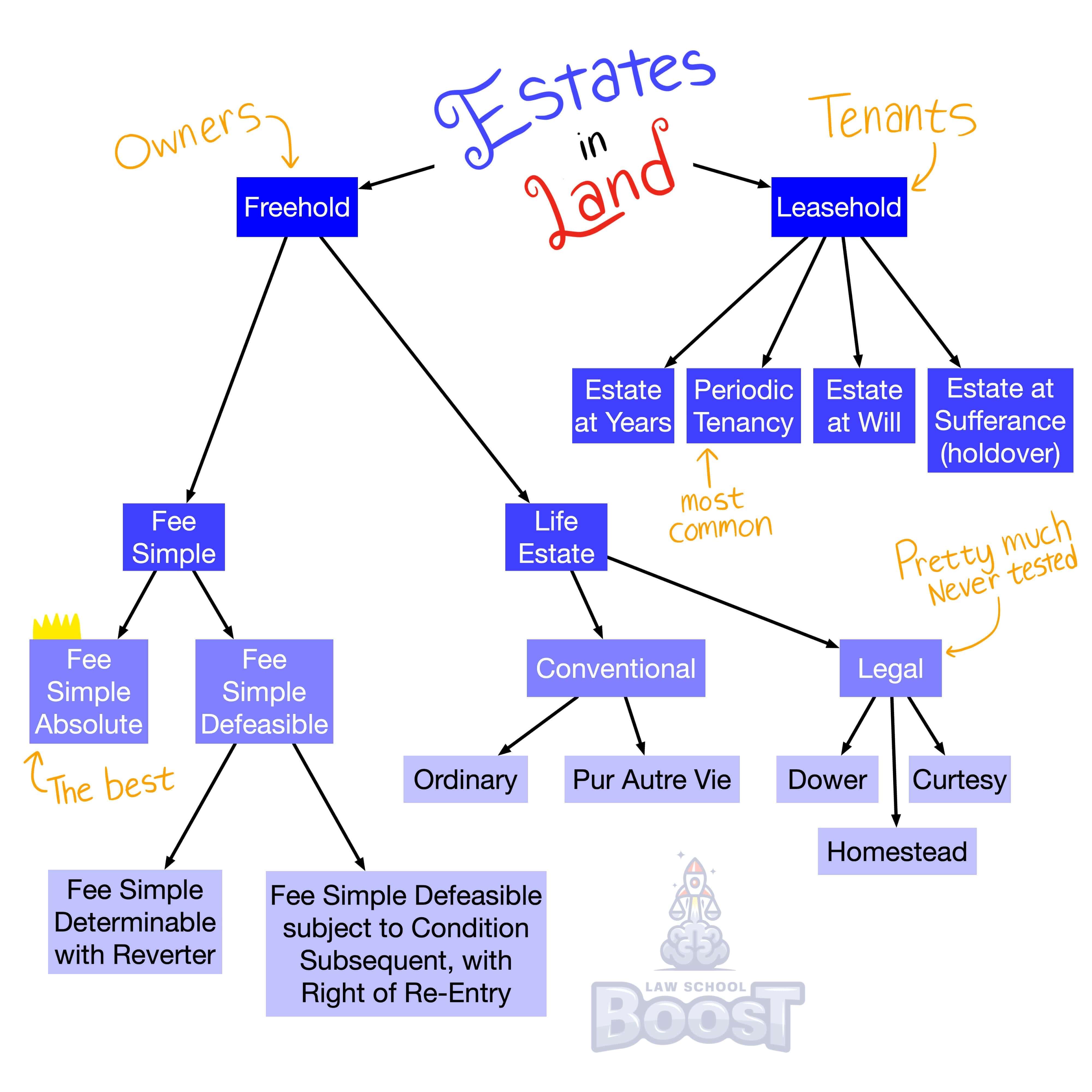
Real Property • Landlord-Tenant
PROP#066
Legal Definition
A new tenancy will not result where (1) the tenant remains in possession for only a few hours after termination and leaves a few articles of personal property, (2) the delay is not the tenant's fault, or (3) it is a seasonal lease.
Plain English Explanation
The purpose of the hold-over doctrine is to recognize the impact that hold-over tenants have on a landlord. In other words, landlords make a living by renting out property they own to people who give them money and it isn't fair for a tenant to disrupt a landlord's business by staying beyond their agreed upon period. However, the law wants to be fair to tenants as well. Thus, the hold-over doctrine will not create a new tenancy in the following hold-over situations:
(1) When the period of "holding over" is only a few hours or so, or if a few items of personal property are left behind. For example, if a lease is to expire at 5pm on March 1st and the tenant is still packing stuff up and doesn't leave until 6pm on March 1st, this doesn't give the landlord the right to bind the tenant to a new lease under the hold-over doctrine. Likewise, if a tenant leaves behind a few shirts in the closet, this isn't enough to trigger the hold-over doctrine. Contrast this to a scenario where a tenant leaves all of their property behind, then this would constitute a hold-over and trigger the hold-over doctrine because it's not up to the landlord to warehouse a tenant's property for free.
(2) If the tenant is holding-over due to reasons that are not their fault, the hold-over doctrine doesn't apply. For example, if tenants are required to move out on February 1st, but a large blizzard dumps 5 feet of snow and prevents anyone from leaving their homes, then it wouldn't be very nice to force the tenants into a new lease.
(3) If the tenant has a seasonal lease, which defines the period of possession as a season and not specific months, then it becomes harder to define when a season has officially ended and when a tenant is "holding-over" into a different season.
(1) When the period of "holding over" is only a few hours or so, or if a few items of personal property are left behind. For example, if a lease is to expire at 5pm on March 1st and the tenant is still packing stuff up and doesn't leave until 6pm on March 1st, this doesn't give the landlord the right to bind the tenant to a new lease under the hold-over doctrine. Likewise, if a tenant leaves behind a few shirts in the closet, this isn't enough to trigger the hold-over doctrine. Contrast this to a scenario where a tenant leaves all of their property behind, then this would constitute a hold-over and trigger the hold-over doctrine because it's not up to the landlord to warehouse a tenant's property for free.
(2) If the tenant is holding-over due to reasons that are not their fault, the hold-over doctrine doesn't apply. For example, if tenants are required to move out on February 1st, but a large blizzard dumps 5 feet of snow and prevents anyone from leaving their homes, then it wouldn't be very nice to force the tenants into a new lease.
(3) If the tenant has a seasonal lease, which defines the period of possession as a season and not specific months, then it becomes harder to define when a season has officially ended and when a tenant is "holding-over" into a different season.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
How do lease covenants affect a landlord-tenant relationship where one party breaches?
How may a landlord waive a covenant prohibiting assignment?
If a leasehold is condemned or taken via eminent domain, what is the effect on a tenant's duty to pay rent?
If an assignment occurs, what is the relationship between the assignee and the landlord?
If a tenant breaches one or more of their duties, what remedies are available to the landlord?
If a tenant violates a covenant against assignment or sublease, what remedies are available to the landlord?
In a landlord-tenant relationship, who has a duty of restoration when the premises being leased are destroyed due to no fault of either party?
In assessing a landlord's tort liability, what six duties does a landlord have to make the premises safe?
In assessing a landlord-tenant issue, what is an assignment?
In assessing a landlord-tenant relationship, what are the landlord's duties?
In assessing a landlord-tenant relationship, what are the tenant's duties?
In assessing a landlord-tenant relationship, what is the result of a tenant's covenant to repair?
What constitutes a constructive eviction?
What constitutes an actual eviction?
What constitutes a partial eviction?
What is a landlord's duty to deliver possession?
What is a landlord's duty to provide quiet enjoyment?
What is a landlord's duty to repair?
What is a leasehold estate?
What is a periodic tenancy and how does it terminate?
What is a retaliatory eviction?
What is a sublease?
What is a tenancy at sufferance and how does it terminate?
What is a tenancy at will and how does it terminate?
What is a tenancy for years and how does it terminate?
What is a tenant's duty to not use the premises for an illegal purpose?
What is a tenant's duty to pay rent, and how does it affect their security deposit?
What is a tenant's duty to repair?
What is the hold-over doctrine?
What is the implied warranty of habitability, and what remedies are available to the tenant if breached?
When does a covenant run with the land?
When does a tenant cause ameliorative waste?
When does a tenant cause permissive waste?
When does a tenant cause voluntary waste?


