🏥
Remedies • Contract - Equitable Remedies
REM#068
Legal Definition
Defenses to rescission include unclean hands and laches. Negligence of the defendant is not a good defense.
Plain English Explanation
When someone wants to undo or cancel a legal agreement (this is called "rescission"), there are certain reasons or defenses they can use to prevent this from happening. Two of these defenses are "unclean hands" and "laches." "Unclean hands" means that the person trying to cancel the agreement has also done something wrong related to the agreement. "Laches" means that the person waited too long to try to cancel the agreement. However, just because the other person was careless or negligent doesn't mean you can cancel the agreement.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Bob sells Sam a car, claiming it has never been in an accident. After Sam buys the car, he discovers it had been in a severe crash and demands rescission of the contract. However, it turns out that Sam, knowing the car's history, only paid half the agreed price, promising to pay the rest later. Result: Sam's demand for rescission may be denied due to the defense of unclean hands, as Sam's own misconduct in the transaction taints his claim.
Hypo 2: Bob sells a piece of land to Sam, misrepresenting its zoning status. Sam, after purchasing, learns that the land cannot be used for the purpose he intended and seeks rescission. Bob counters by claiming that Sam waited too long to bring the action, and the value of the land has significantly decreased in the meantime. Result: The court may deny rescission under the doctrine of laches if it finds that Sam's delay in seeking rescission caused undue prejudice to Bob.
Hypo 3: Bob sells Sam a vintage watch, assuring him it's a rare collector's item. Sam later discovers the watch is a replica and seeks rescission. However, Bob argues that Sam negligently failed to authenticate the watch before purchase. Result: Bob's defense of negligence will not succeed, as negligence is not a valid defense to rescission; Sam is still entitled to rescind the contract.
Hypo 4: Bob sells Sam a boat with a minor scratch that Bob disclosed and discounted the price for. Sam, unhappy with the purchase, seeks rescission, claiming the scratch is more significant than he thought. Result: Sam cannot rescind the contract based on this minor issue, as the rule about rescission wouldn’t apply in a case where the defect was disclosed, and no significant misconduct or prejudice is involved.
Hypo 2: Bob sells a piece of land to Sam, misrepresenting its zoning status. Sam, after purchasing, learns that the land cannot be used for the purpose he intended and seeks rescission. Bob counters by claiming that Sam waited too long to bring the action, and the value of the land has significantly decreased in the meantime. Result: The court may deny rescission under the doctrine of laches if it finds that Sam's delay in seeking rescission caused undue prejudice to Bob.
Hypo 3: Bob sells Sam a vintage watch, assuring him it's a rare collector's item. Sam later discovers the watch is a replica and seeks rescission. However, Bob argues that Sam negligently failed to authenticate the watch before purchase. Result: Bob's defense of negligence will not succeed, as negligence is not a valid defense to rescission; Sam is still entitled to rescind the contract.
Hypo 4: Bob sells Sam a boat with a minor scratch that Bob disclosed and discounted the price for. Sam, unhappy with the purchase, seeks rescission, claiming the scratch is more significant than he thought. Result: Sam cannot rescind the contract based on this minor issue, as the rule about rescission wouldn’t apply in a case where the defect was disclosed, and no significant misconduct or prejudice is involved.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
How does election of remedies affect a claim for rescission?
If a contract has a liquidated damages clause, is specific performance still an option?
What are common defenses to specific performance?
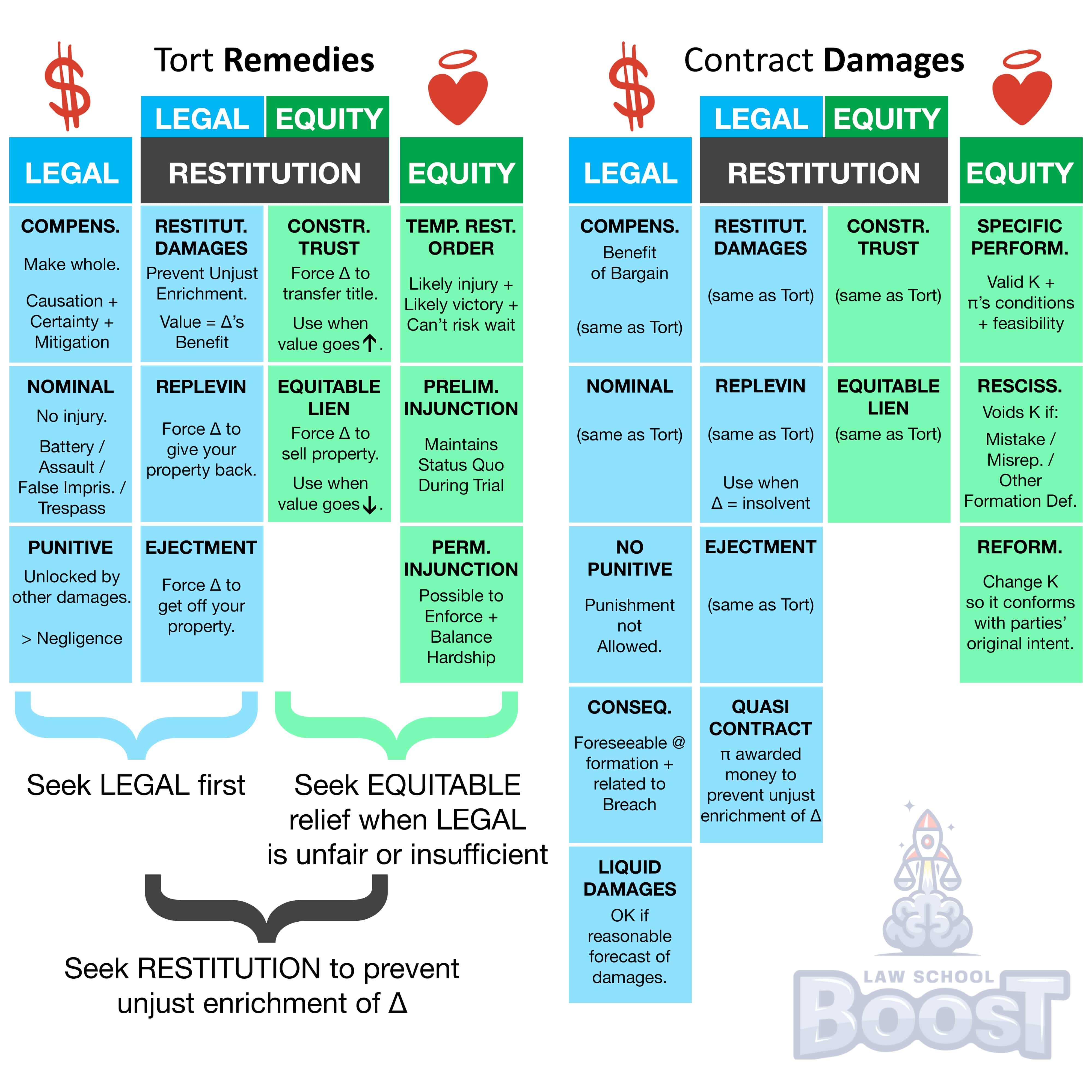
What are equitable remedies in contract?
What are the defenses to formation?
What happens if a plaintiff is entitled to rescission but has already performed?
What is reformation?
What is rescission?
What is specific performance and when it is applicable?
What is the part performance exception to the Statute of Frauds?
What type of mutual mistake is sufficient for rescission?
When applying specific performance to a land purchase contract, what happens if a buyer breaches a "time is of the essence" clause with a forfeiture clause?
When applying specific performance to a land purchase contract, what happens if the quantity of land is in dispute?
When assessing reformation, what constitutes sufficient grounds?
When assessing specific performance, how do courts weigh feasibility of enforcement?
When assessing specific performance to acquire a unique piece of property, when is uniqueness tested?
When assessing specific performance, what must the status be of a plaintiff's contractual conditions?
When assessing specific performance, why are money damages sometimes an inadequate legal remedy?
When assessing whether money damages are inadequate for specific performance, why does it matter whether a piece of property is unique and what kind of property is always unique?
When is personal property considered unique enough to trigger specific performance?
Will courts grant rescission for a unilateral mistake?


