🏥
Remedies • Contract - Equitable Remedies
REM#072
Legal Definition
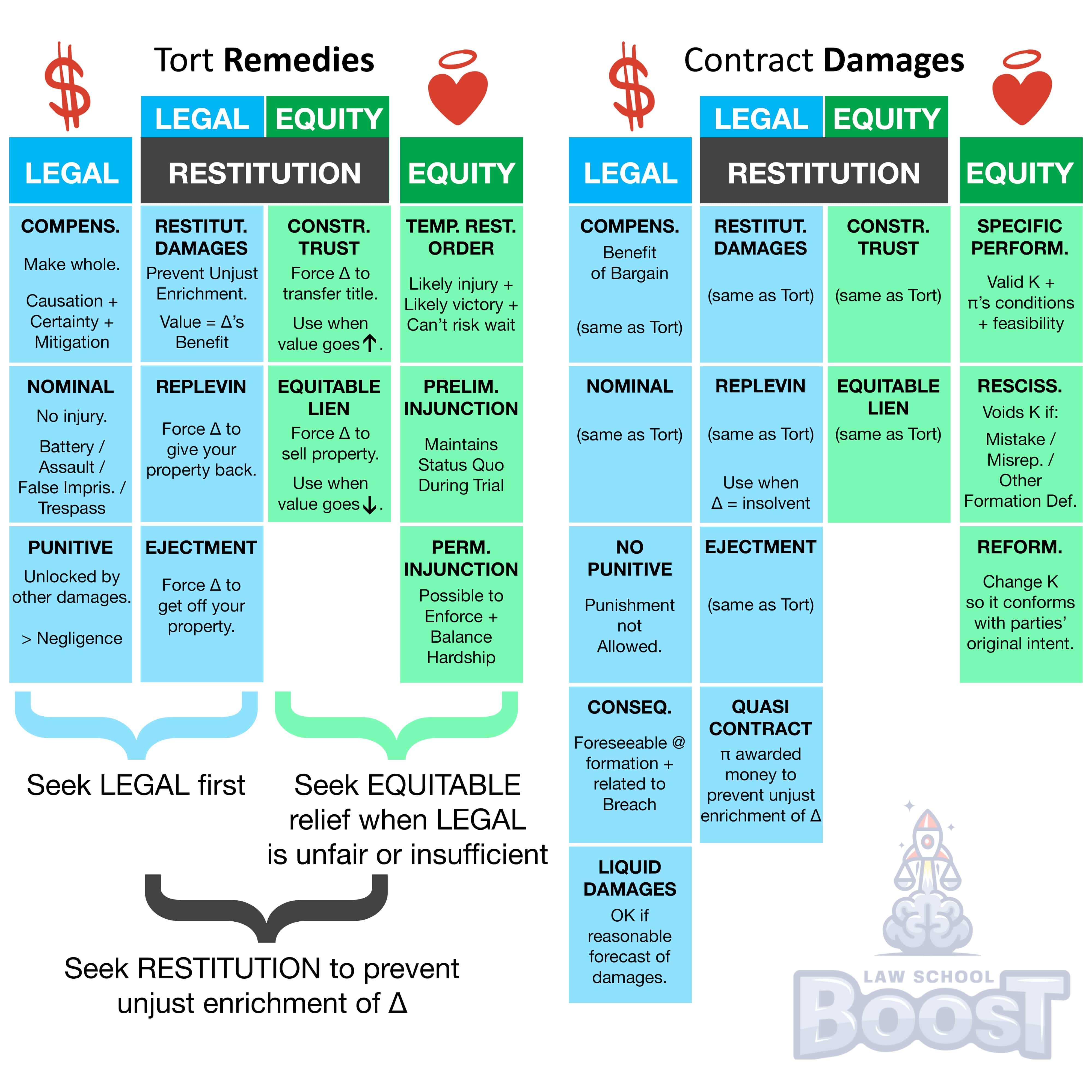
Reformation will be granted where the parties made a mutual mistake, or where one party made a misrepresentation (in which case, the rewriting will reflect the expressed intent of the parties).
In contrast, reformation is generally not granted in the case of unilateral mistake, unless the non-mistaken party knows of the mistake.
In contrast, reformation is generally not granted in the case of unilateral mistake, unless the non-mistaken party knows of the mistake.
Plain English Explanation
When people make an agreement, sometimes there are mistakes in the written document. If both parties made the mistake together, or if one person lied or misled the other, the court can change the written document to match what they both originally wanted. However, if only one person made a mistake and the other person didn't know about it, the court usually won't change the document. The reason for this rule is to make sure that written agreements are fair and reflect what both parties really wanted.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Bob and Sam agree to sell a car for $5,000. When writing the agreement, both mistakenly write $500. Result: The court changes the agreement to $5,000 because both made a mutual mistake.
Hypo 2: Bob and Sam agree to a contract where Sam will paint Bob's house blue. Bob mistakenly writes "green" in the contract. Sam genuinely thinks Bob changed his mind and doesn't realize it's a mistake. Result: The court won't change the agreement because only Bob made the mistake and Sam didn't know it was a mistake.
Hypo 2: Bob and Sam agree to a contract where Sam will paint Bob's house blue. Bob mistakenly writes "green" in the contract. Sam genuinely thinks Bob changed his mind and doesn't realize it's a mistake. Result: The court won't change the agreement because only Bob made the mistake and Sam didn't know it was a mistake.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
How does election of remedies affect a claim for rescission?
If a contract has a liquidated damages clause, is specific performance still an option?
What are common defenses to specific performance?
What are defenses to rescission?
What are equitable remedies in contract?
What are the defenses to formation?
What happens if a plaintiff is entitled to rescission but has already performed?
What is reformation?
What is rescission?
What is specific performance and when it is applicable?
What is the part performance exception to the Statute of Frauds?
What type of mutual mistake is sufficient for rescission?
When applying specific performance to a land purchase contract, what happens if a buyer breaches a "time is of the essence" clause with a forfeiture clause?
When applying specific performance to a land purchase contract, what happens if the quantity of land is in dispute?
When assessing specific performance, how do courts weigh feasibility of enforcement?
When assessing specific performance to acquire a unique piece of property, when is uniqueness tested?
When assessing specific performance, what must the status be of a plaintiff's contractual conditions?
When assessing specific performance, why are money damages sometimes an inadequate legal remedy?
When assessing whether money damages are inadequate for specific performance, why does it matter whether a piece of property is unique and what kind of property is always unique?
When is personal property considered unique enough to trigger specific performance?
Will courts grant rescission for a unilateral mistake?


