🏥
Remedies • Contract - Legal Remedies
REM#041
Legal Definition
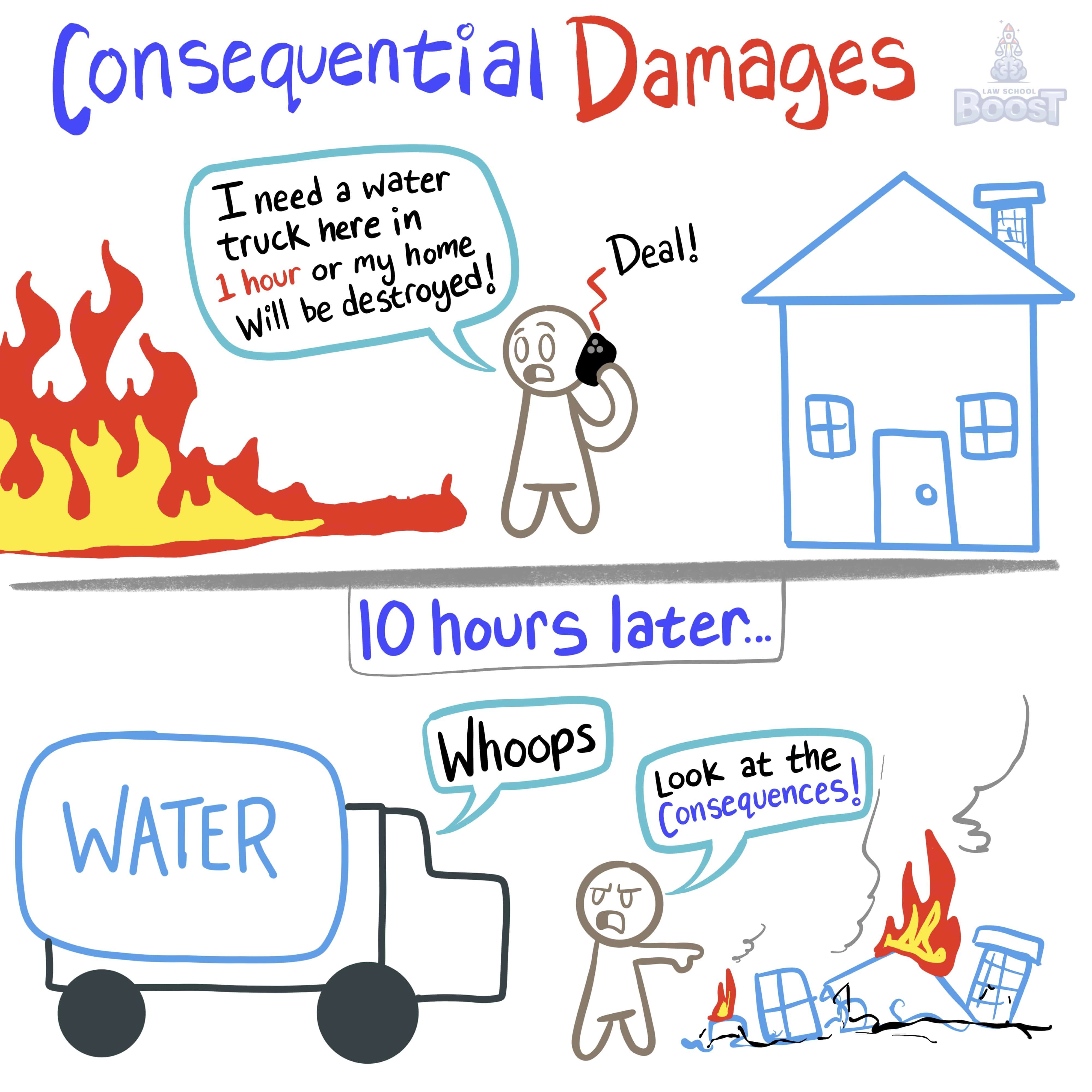
Consequential damages are available for related damages that were foreseeable at the time of formation.
Plain English Explanation
Consequential damages in contract law refer to the compensation given for losses that were expected to happen if the contract was broken. In other words, if two people make a deal and one person thinks, "If this deal goes wrong, I might face these specific problems," and the other person is aware of these potential problems, then the person causing the problems might have to pay for them. The rule exists to make sure that people are held responsible for the predictable harm they cause when they don't stick to their agreements.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Bob sells Sam a special machine for Sam's ice cream shop. Bob knows that without this machine, Sam can't make ice cream and will lose money every day. Bob promises to deliver the machine on Monday, but he delivers it on Friday. Because of this delay, Sam loses money from not selling ice cream for four days. Result: Sam can claim consequential damages from Bob for the money he lost, because Bob knew that a delay would cause Sam to lose sales.
Hypo 2: Bob agrees to provide internet service to Sam's online store. Bob knows that if the internet goes down, Sam's store can't make sales. One day, the internet service stops working for 24 hours, causing Sam to lose sales. Result: Sam can claim consequential damages from Bob for the sales he lost during the internet outage, because it was foreseeable that a lack of internet would harm Sam's business. Note, however, that many internet providers have contractual language that either (a) doesn't guarantee any uptime, or (b) doesn't guarantee 100% update for this exact reason.
Hypo 2: Bob agrees to provide internet service to Sam's online store. Bob knows that if the internet goes down, Sam's store can't make sales. One day, the internet service stops working for 24 hours, causing Sam to lose sales. Result: Sam can claim consequential damages from Bob for the sales he lost during the internet outage, because it was foreseeable that a lack of internet would harm Sam's business. Note, however, that many internet providers have contractual language that either (a) doesn't guarantee any uptime, or (b) doesn't guarantee 100% update for this exact reason.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
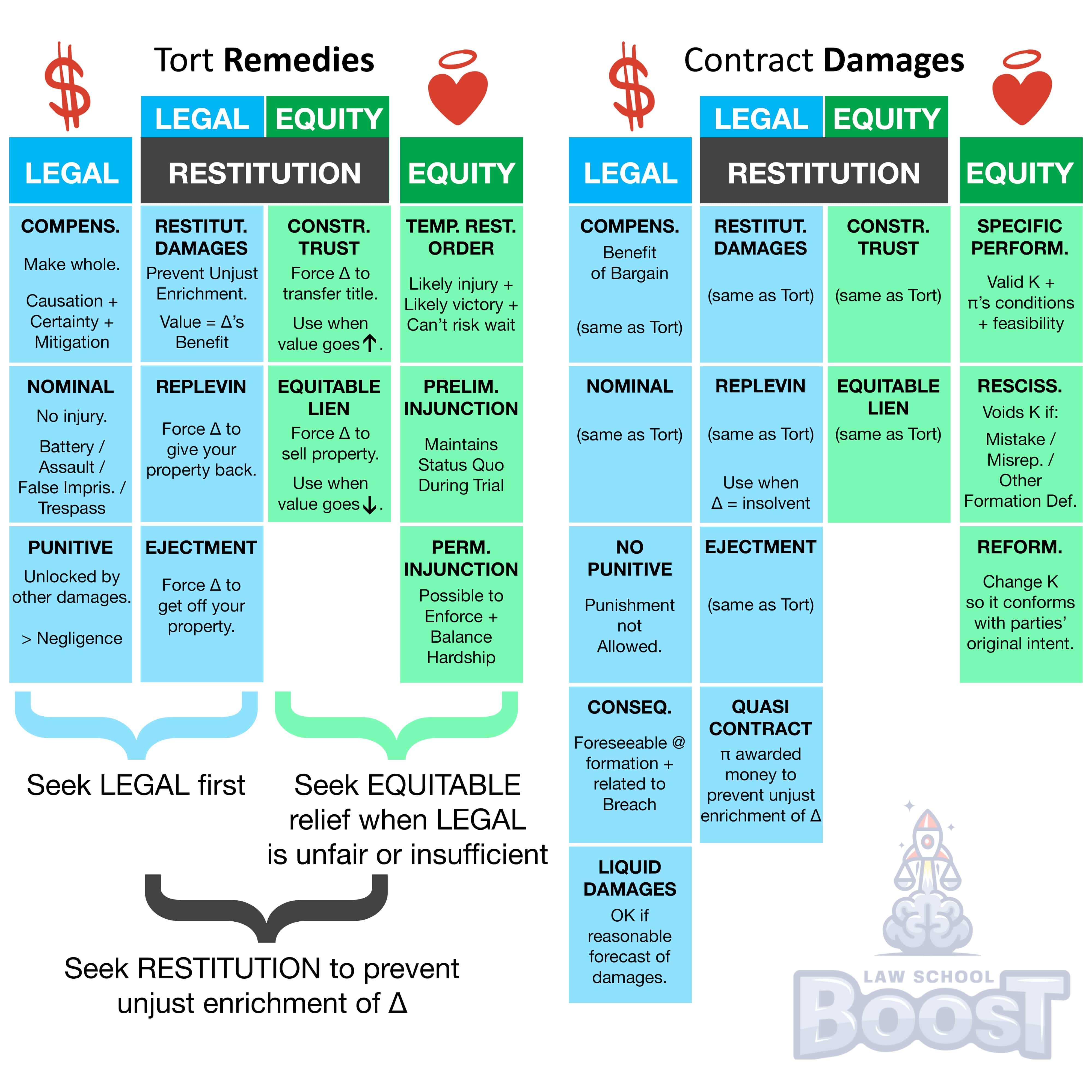
In assessing contract legal remedies, are nominal damages permitted?
In assessing contract legal remedies, are punitive damages permitted?
In assessing contract legal remedies, what are compensatory damages?
In assessing contract legal remedies, what are expectation damages?
In assessing contract legal remedies, what are incidental damages?
In assessing contract legal remedies, what are liquidated damages and when are they permissible?
What are legal remedies in contract?
What elements are required to prove legal remedies in contract?
What is the result of having a liquidated damages provision that is too excessive?


