🏥
Remedies • Contract - Legal Remedies
REM#042
Legal Definition
Incidental damages represent certain expenses incurred as a result of the breach (e.g., storage and shipping costs).
Plain English Explanation
Many business deals are complex (even if they don't seem to be) with multiple individuals or resources working together in order to complete some job or task. For example, imagine if you were planning a large party and wanted to serve seafood. You realize you don't have a large fridge to hold the seafood, so you specifically contract with the seller to deliver your food on the specific day of your event at a specific time before it is to be eaten. However, the company ends up delivering your seafood two days earlier. You're now stuck with a bunch of food that is at risk of going bad. Rather than let it go bad, you may opt to rent some chilled storage space at a local grocery store to hold it until your party. This would cost money that you wouldn't have had to pay if the seller delivered on the correct day. These costs are considered "incidental damages" in contract law, and you'd be allowed to sue the seller to cover them since they caused them as a result of their contract breach.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Sam hires Bob to fumigate his house and kill an insect infestation. Bob promises to finish the job in three days. However, Bob takes a week to complete it. During this time, Sam had to stay in a hotel and also had to pay for the storage of his furniture. Result: The hotel and storage costs are incidental damages because they are extra expenses Sam had to bear due to Bob's delay. Bob would need to compensate Sam for these additional costs.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
In assessing contract legal remedies, are nominal damages permitted?
In assessing contract legal remedies, are punitive damages permitted?
In assessing contract legal remedies, what are compensatory damages?
In assessing contract legal remedies, what are consequential damages?
In assessing contract legal remedies, what are expectation damages?
In assessing contract legal remedies, what are liquidated damages and when are they permissible?
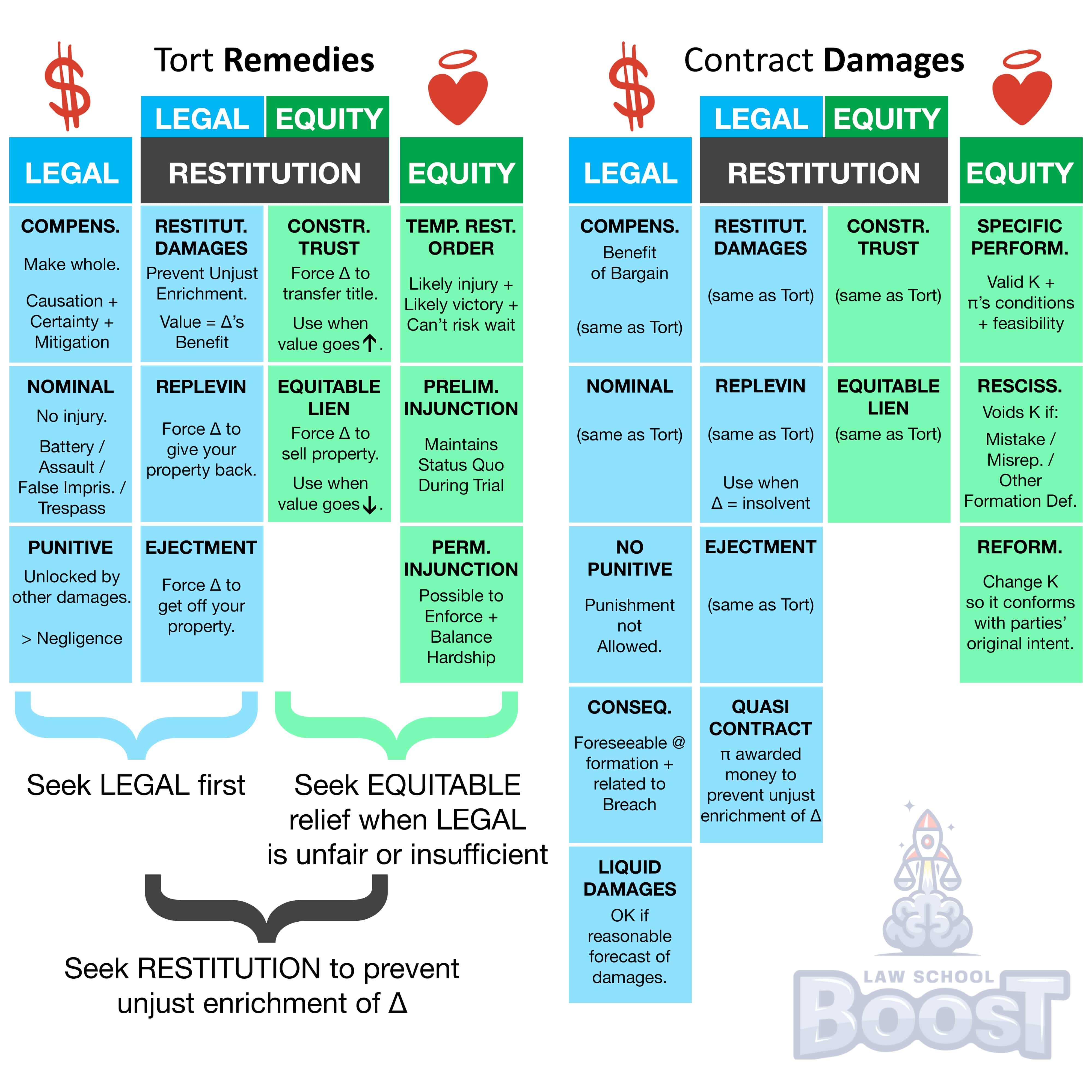
What are legal remedies in contract?
What elements are required to prove legal remedies in contract?
What is the result of having a liquidated damages provision that is too excessive?


