🤤
Civil Procedure • Subject Matter Jurisdiction
CIVPRO#010
Legal Definition
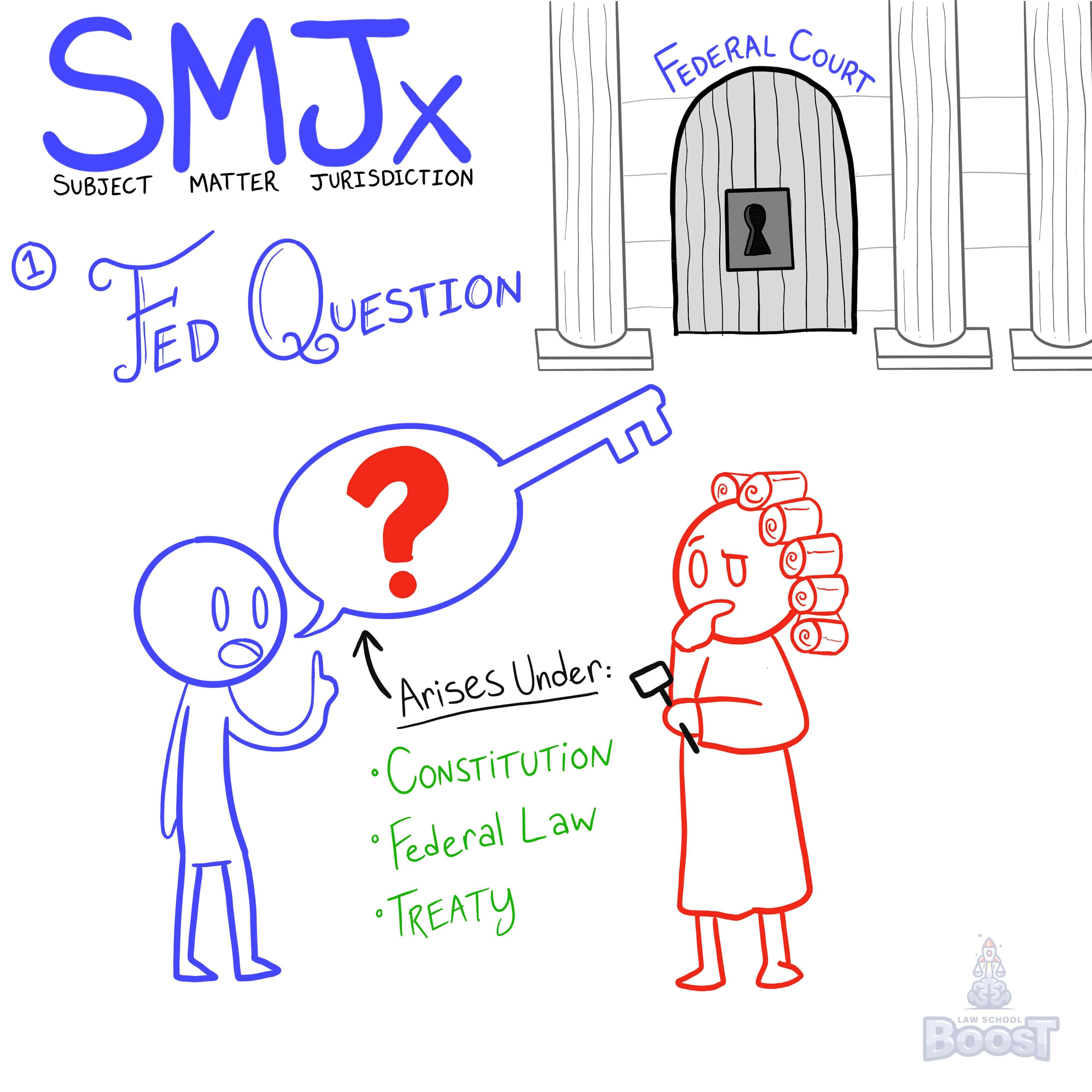
Subject matter jurisdiction based on a federal question involves a claim or cause of action—not an anticipated defense—that arises under the US Constitution, federal law, or a treaty. A federal question must appear on the face of a well-pleaded complaint.
Plain English Explanation
Courts provide judgments, and judgements are, put simply, a type of answer to a question. Many times the question being asked is, "Who is liable?" For example, when you are in a car accident, you may sue the person who you feel is responsible for your damage. You are basically asking the court, "Under these facts, is the defendant responsible for paying for the damages?" Ideally, the answer from the court will be, "Yup."
When you think of courts in this way, then "federal questions" should be easier to understand. Put simply, a "federal question" is a question that may be answered in federal court because it involves something federally related, like a federal law, the US constitution, a treaty, etc.
When you think of courts in this way, then "federal questions" should be easier to understand. Put simply, a "federal question" is a question that may be answered in federal court because it involves something federally related, like a federal law, the US constitution, a treaty, etc.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Sam works for Bob. One day, Bob suddenly fires Sam and refuses to pay him for his hours worked that day. Sam tries to sue Bob in federal court. Result: Sam won't be able to sue Bob in federal court, because the subject matter of his suit is not within the subject matter jurisdiction of federal court. This is a wage claim, which would be a simple labor issue that the state is equipped to handle.
Hypo 2: Sam works for Bob. One day, Bob suddenly fires Sam. When Sam asks "Why?" Bob responds, "Because you're black and I don't want a black employee." Sam tries to sue Bob in federal court. Result: There are plenty of states with laws that make it illegal to fire someone based on their race, and it would be appropriate for Sam to sue Bob in their state's court. However, there are also federal laws that make this illegal. This means that the subject matter of Sam's suit unlocks the "Federal Question" door, allowing Sam to sue Bob in federal court.
Hypo 2: Sam works for Bob. One day, Bob suddenly fires Sam. When Sam asks "Why?" Bob responds, "Because you're black and I don't want a black employee." Sam tries to sue Bob in federal court. Result: There are plenty of states with laws that make it illegal to fire someone based on their race, and it would be appropriate for Sam to sue Bob in their state's court. However, there are also federal laws that make this illegal. This means that the subject matter of Sam's suit unlocks the "Federal Question" door, allowing Sam to sue Bob in federal court.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
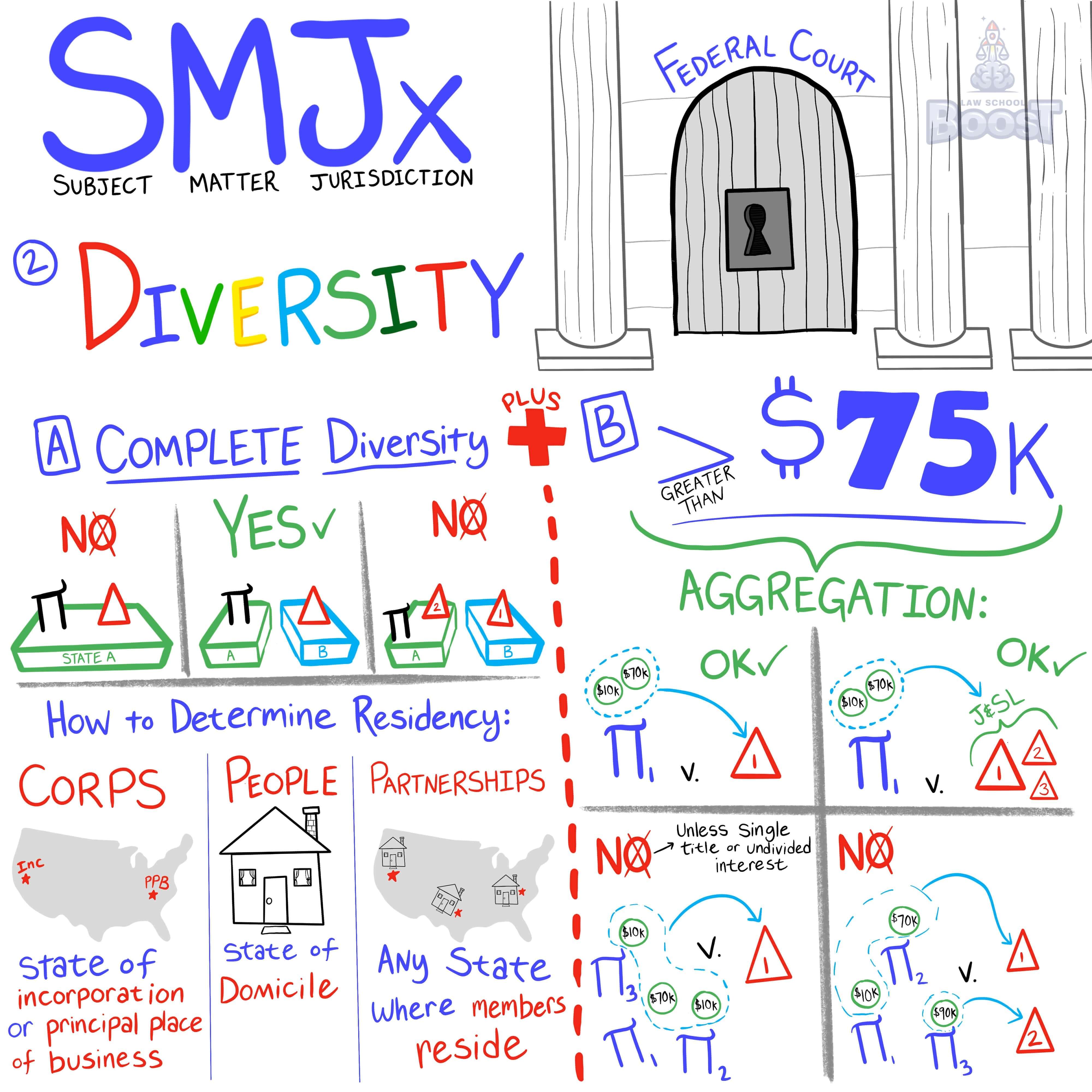
How can subject matter jurisdiction be based on diversity of citizenship?
How is citizenship determined under subject matter jurisdiction?
What is subject matter jurisdiction?
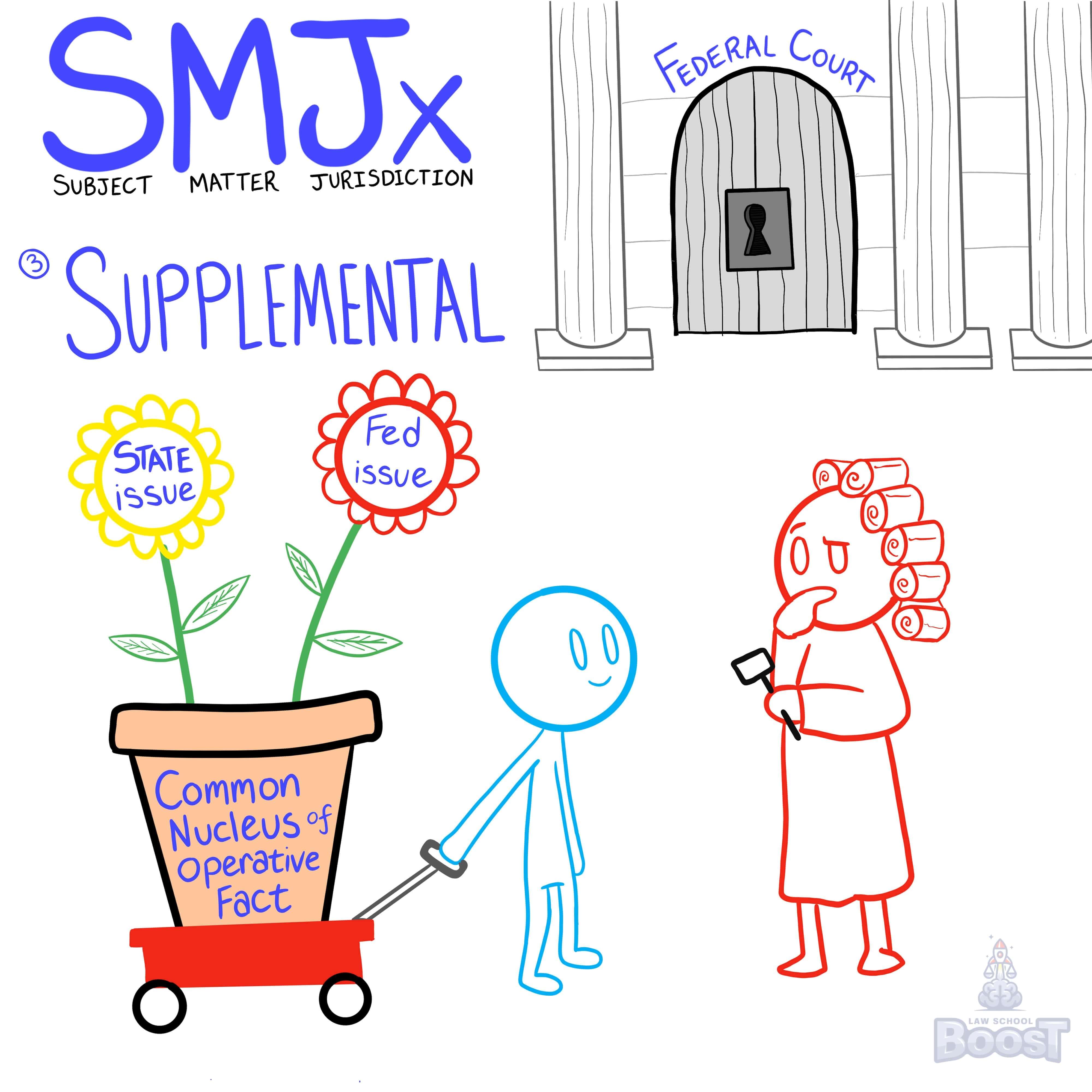
What is supplemental jurisdiction?
What types of cases will California courts exercise general subject matter jurisdiction over?
When is aggregation of damages under a diversity claim allowed and not allowed?
When may a federal court hear a state claim?


