😀
Real Property • Present Possessory Estates
PROP#002
Legal Definition
The fee simple absolute is the largest estate recognized by law, and can be sold, divided, devised, and inherited. It is indefinite, or potentially indefinite in duration, and presumed in the absence of contrary intent.
Plain English Explanation
A fee simple absolute or FSA (sometimes just called fee simple) is the king of estates. In other cards, you will learn how property rights are like a "bundle of sticks," which can be divided and sold. An FSA is the entire bundle of sticks. It means that you own a piece of land completely and unquestionably, without limitation. An FSA can be divided into lesser estates which are not nearly as valuable and, like Voltron, lesser interests can sometimes be combined back into the FSA.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Oz conveys Blackacre to Ann. Result: Ann has received all of the rights that Oz has in Blackacre. Assuming Oz had a fee simple interest in Blackacre, then it is presumed that a fee simple interest has passed to Ann.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
How is a fee simple determinable created?
How is a fee simple subject to condition subsequent created?
In assessing a present possessory estate, what is affirmative waste?
In assessing a present possessory estate, what is ameliorative waste?
In assessing a present possessory estate, what is permissive waste?
What are the 3 types of waste a life estate holder may commit?
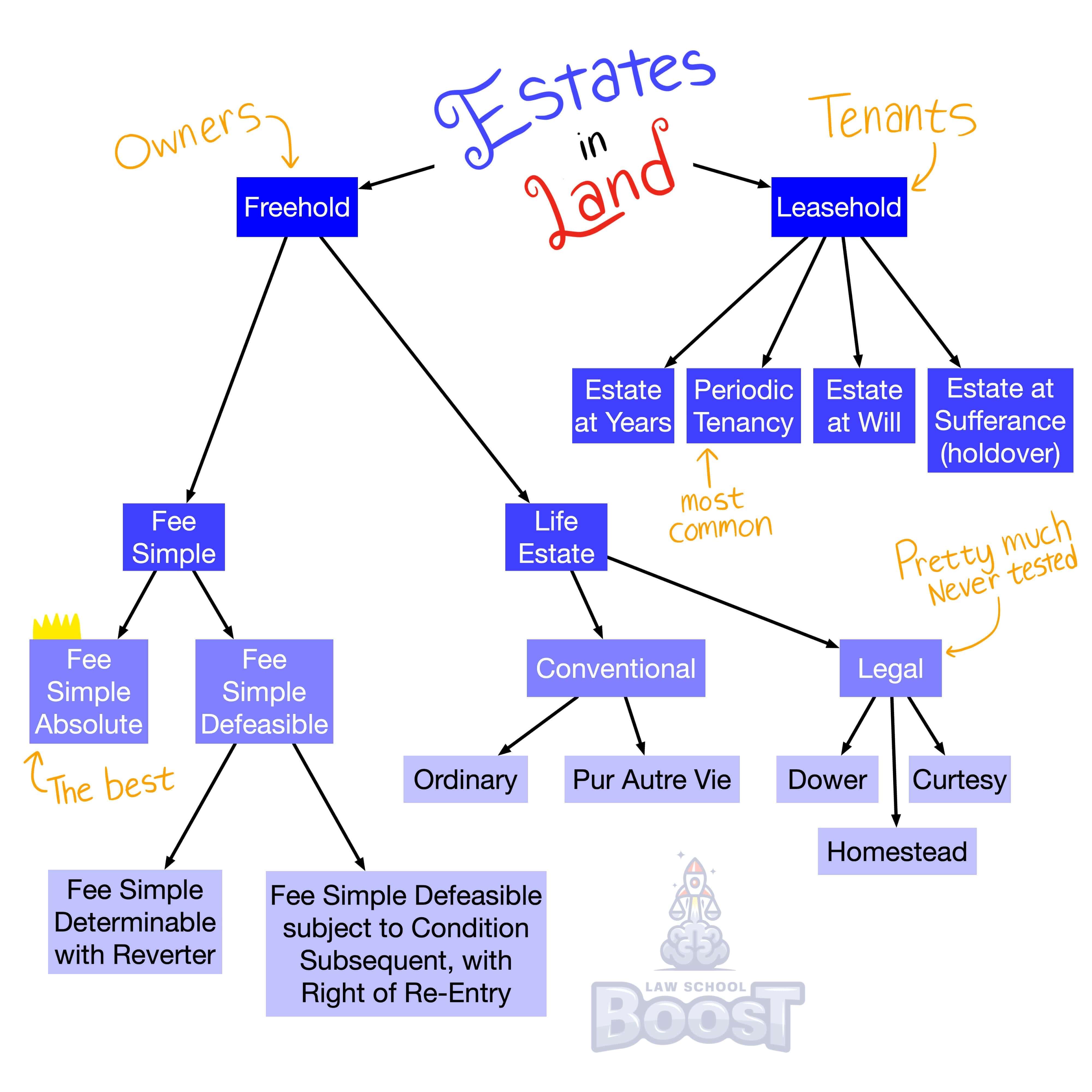
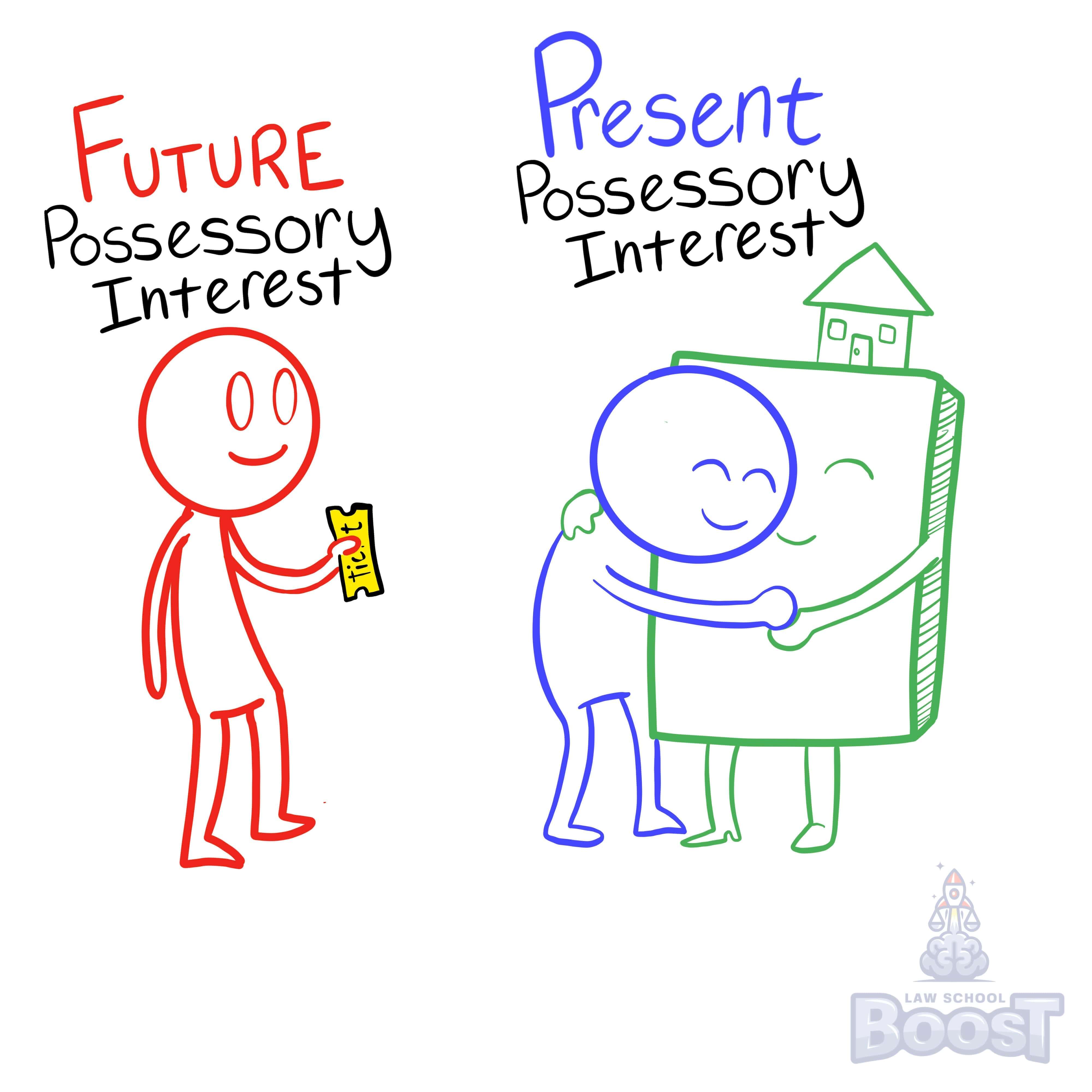
What are the present possessory estates?
What happens when a life estate holder renounces his interest?
What is a defeasible fee?
What is a fee simple subject to executory interest?
What is a fee tail, how is it created, and what is the result of its creation in most jurisdictions today?
What is a life estate?
What is a life estate pur autre vie and how is it created?
What rights and duties do the holder of a life estate have?
What will a court do if it is not clear whether someone intended to create a fee simple determinable or subject to condition subsequent?


