😀
Real Property • Present Possessory Estates
PROP#005
Legal Definition
A fee simple subject to condition subsequent is created by words of condition, such as "upon condition that," "provided that," "but if," or "if it happens that." It is followed by a right of entry, which must be expressly reserved and does not automatically terminate the estate. Instead, the grantor must take some action upon the happening of the stated condition. It is devisable, descendible, and transferable.
Plain English Explanation
One of the biggest questions people want to know when they get an interest in land is "How long do I own it?" A fee simple subject to condition subsequent is a fee simple that can be defeated by a subsequent condition (i.e., a condition that may happen at some point in the future). In other words, when you are reading the fact pattern, look for language like:
- "upon condition that"
-"provided that"
-"but if" or
-"if it happens that"
This type of language lets you know "this interest in land isn't forever."
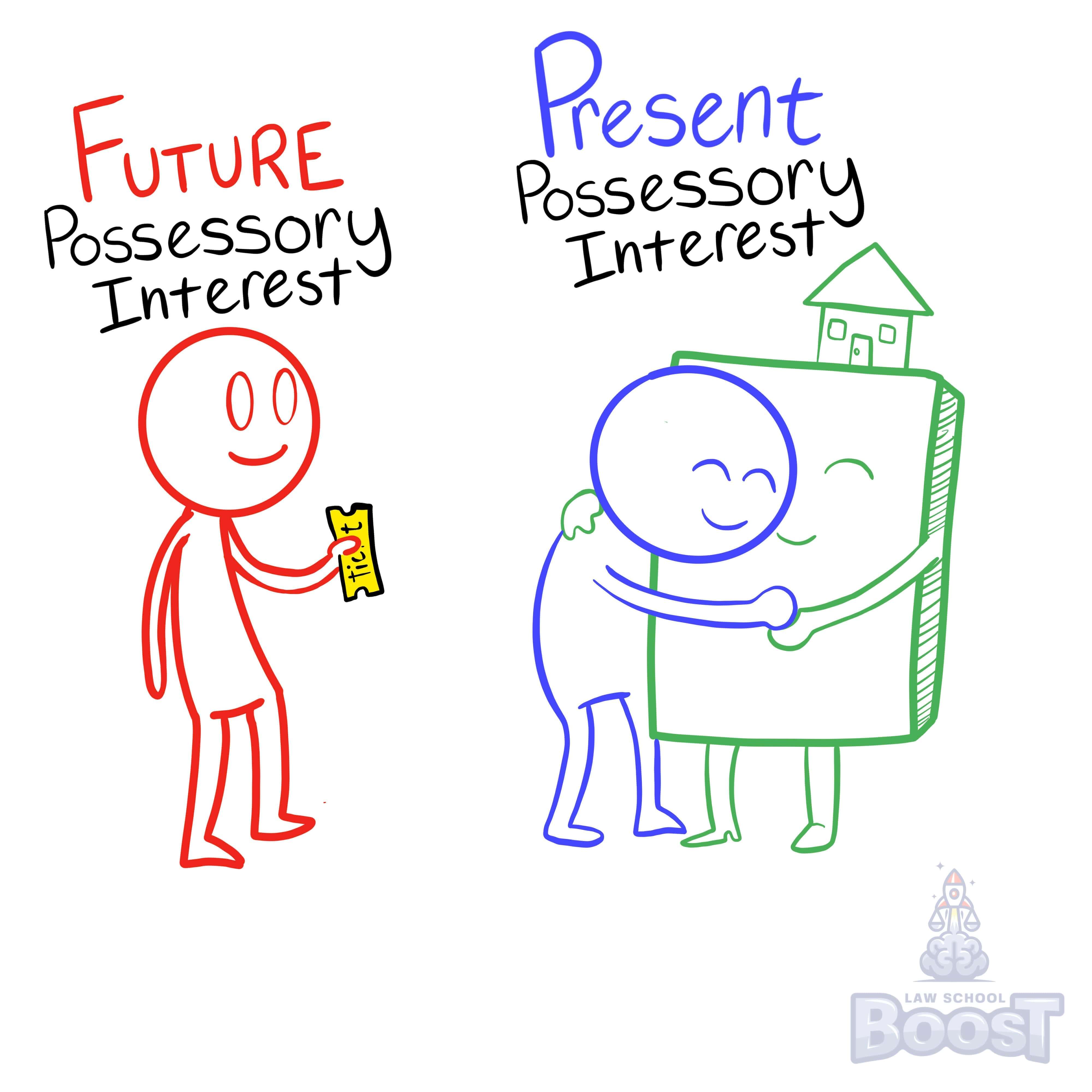
It's also important to know that a fee simple subject to condition subsequent is followed by a right of entry. When it comes to figuring out property conveyances, you need to remember that someone must always own the land, so you must always figure out who currently owns the land and who owns it next. "Followed by a right of entry" means that if the condition occurs, the original grantor (or their heirs) have a right to take the land back. Note that this is different than a fee simple determinable, where the land automatically goes back to the grantor. Also, note that the grantor must explicitly include this right in their conveyance, otherwise it does not apply.
- "upon condition that"
-"provided that"
-"but if" or
-"if it happens that"
This type of language lets you know "this interest in land isn't forever."
It's also important to know that a fee simple subject to condition subsequent is followed by a right of entry. When it comes to figuring out property conveyances, you need to remember that someone must always own the land, so you must always figure out who currently owns the land and who owns it next. "Followed by a right of entry" means that if the condition occurs, the original grantor (or their heirs) have a right to take the land back. Note that this is different than a fee simple determinable, where the land automatically goes back to the grantor. Also, note that the grantor must explicitly include this right in their conveyance, otherwise it does not apply.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Oz conveys Blackacre "to Amy and her heirs, but if marijuana is ever consumed on the premises, then Oz or his heirs may enter and terminate the estate." Result: Amy has been given a fee simple in Blackacre subject to condition subsequent. What is that subsequent condition? Someone consuming marijuana. If one day Amy decides to eat some marijuana space brownies, then Oz (or his heirs) have the right of entry, which allows them to come onto the land and kick Amy out. However, it's possible that Amy may consume marijuana but Oz (or his heirs) opt to not kick her out. It is not automatic, and must be intentional.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
How is a fee simple determinable created?
In assessing a present possessory estate, what is affirmative waste?
In assessing a present possessory estate, what is ameliorative waste?
In assessing a present possessory estate, what is permissive waste?
What are the 3 types of waste a life estate holder may commit?
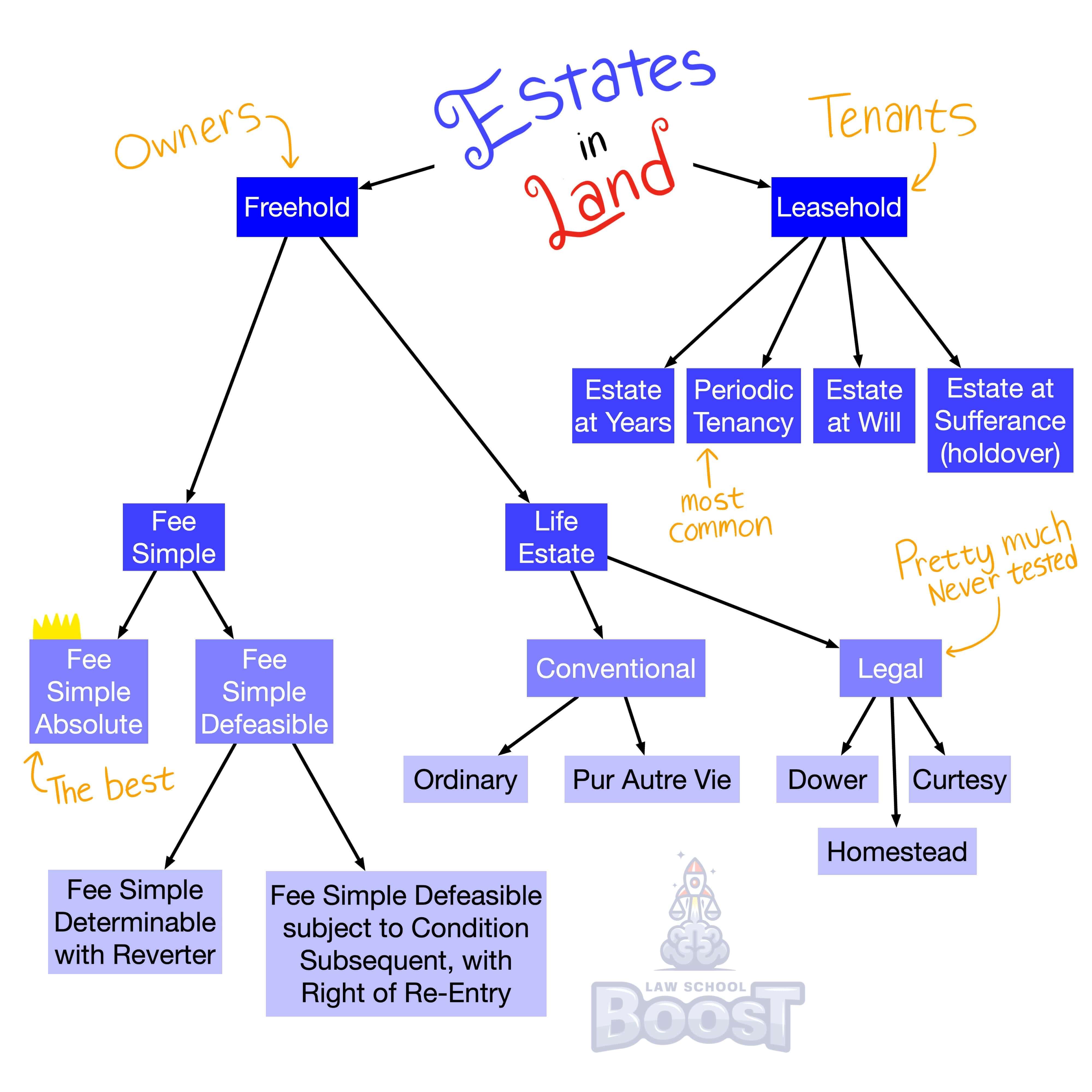
What are the present possessory estates?
What happens when a life estate holder renounces his interest?
What is a defeasible fee?
What is a fee simple absolute?
What is a fee simple subject to executory interest?
What is a fee tail, how is it created, and what is the result of its creation in most jurisdictions today?
What is a life estate?
What is a life estate pur autre vie and how is it created?
What rights and duties do the holder of a life estate have?
What will a court do if it is not clear whether someone intended to create a fee simple determinable or subject to condition subsequent?


