😀
Real Property • Security Interests in Real Estate
PROP#225
Legal Definition
A buyer at a foreclosure sale takes subject to a senior interest, but is not personally liable on the senior debt. If unpaid, the senior creditor will foreclose against the land, so the buyer has incentive to pay off the senior interest.
Plain English Explanation
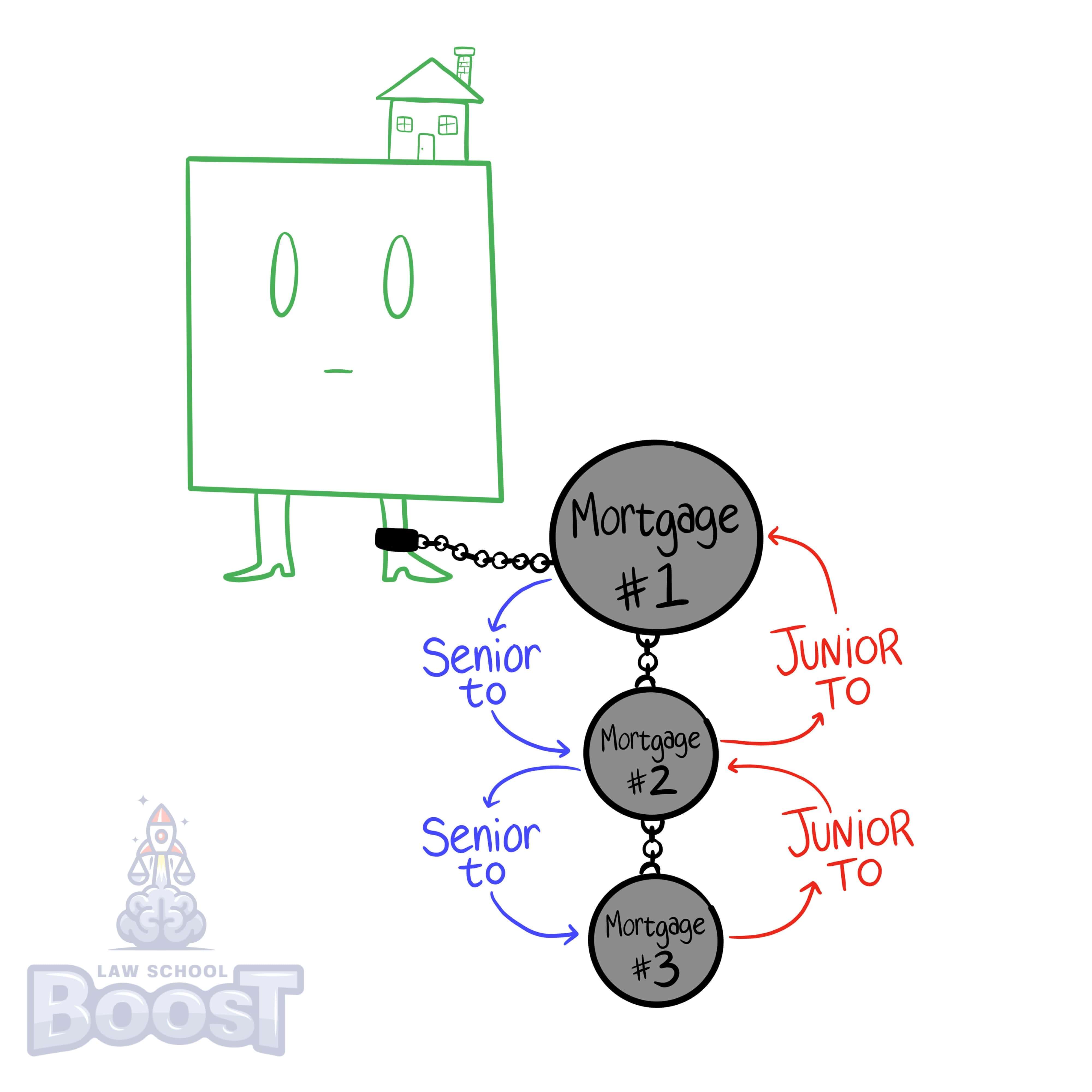
Imagine a mortgage as being a single link of chain that attaches to a property, weighing it down. Each additional mortgage adds another chain link to the link above it. Imagine 3 mortgages on a property. The top link is senior to the bottom 2 junior links. Similarly, the middle link is junior to the top link, but senior to the bottom link.
When a mortgage forecloses on a property, it only affects the junior links that hang from it. Senior mortgages are left alone and follow the property as it is foreclosed on and sold.
When a mortgage forecloses on a property, it only affects the junior links that hang from it. Senior mortgages are left alone and follow the property as it is foreclosed on and sold.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Amy owns Whiteacre. On January 1, Amy gets a mortgage from Bob. On January 2, Amy gets a mortgage from Carl. On January 3, Amy gets a mortgage from Dan. Amy struggles to keep up with her payments to Bob, Carl, and Dan. After a few months, Amy defaults on her mortgage to Carl. Carl forecloses on Whiteacre and notifies Dan. Ed purchases the foreclosure sale, which frees Whiteacre from both Carl and Dan's mortgage. However, Ed takes Whiteacre with Bob's mortgage still attached. Note that this doesn't mean Ed is personally liable to pay the mortgage to Bob -- only Amy is still on the hook for that. However, Ed is incentivized to pay the mortgage because if he doesn't, Bob has the right to foreclose on Whiteacre.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
How do states treat a mortgage without a note?
How do states treat a note without a mortgage?
How is a mortgage's priority determined?
How may a party be a holder in due course of a note?
In lieu of foreclosure, what do many installment contracts prefer and how do courts address this alternative?
Under which theories may a mortgagee take possession of a property and begin receiving rents before foreclosure?
What are the 5 types of security interests in real estate?
What are the benefits of the holder in due course status?
What are the limitations of a junior interest?
What are the methods of transferring a note?
What interests does a foreclosure destroy?
What is a deficiency judgment?
What is a due on sales clause?
What is a foreclosure?
What is an installment land contracts?
What is a receivership?
What is a redemption in equity?
What is a statutory redemption?
What is the distribution order of proceeds from a foreclosure?
What is the result of a grantee assuming the mortgage?
What liabilities are associated with a mortgaged property that is transferred to another party?
What occurs in intermediate theory states?
What occurs in lien theory states?
What occurs in title theory states?
What security interests exist under a absolute deed?
What security interests exist under a deed of trust?
What security interests exist under a installment land contract?
What security interests exist under a mortgage?
What security interests exist under a sale-leaseback?
Who may transfer their interest in a mortgage?


