🤔
Contracts • Contract Formation
K#030
Legal Definition
Additional or different terms in an acceptance are mere proposals and the terms of the offer govern.
Plain English Explanation
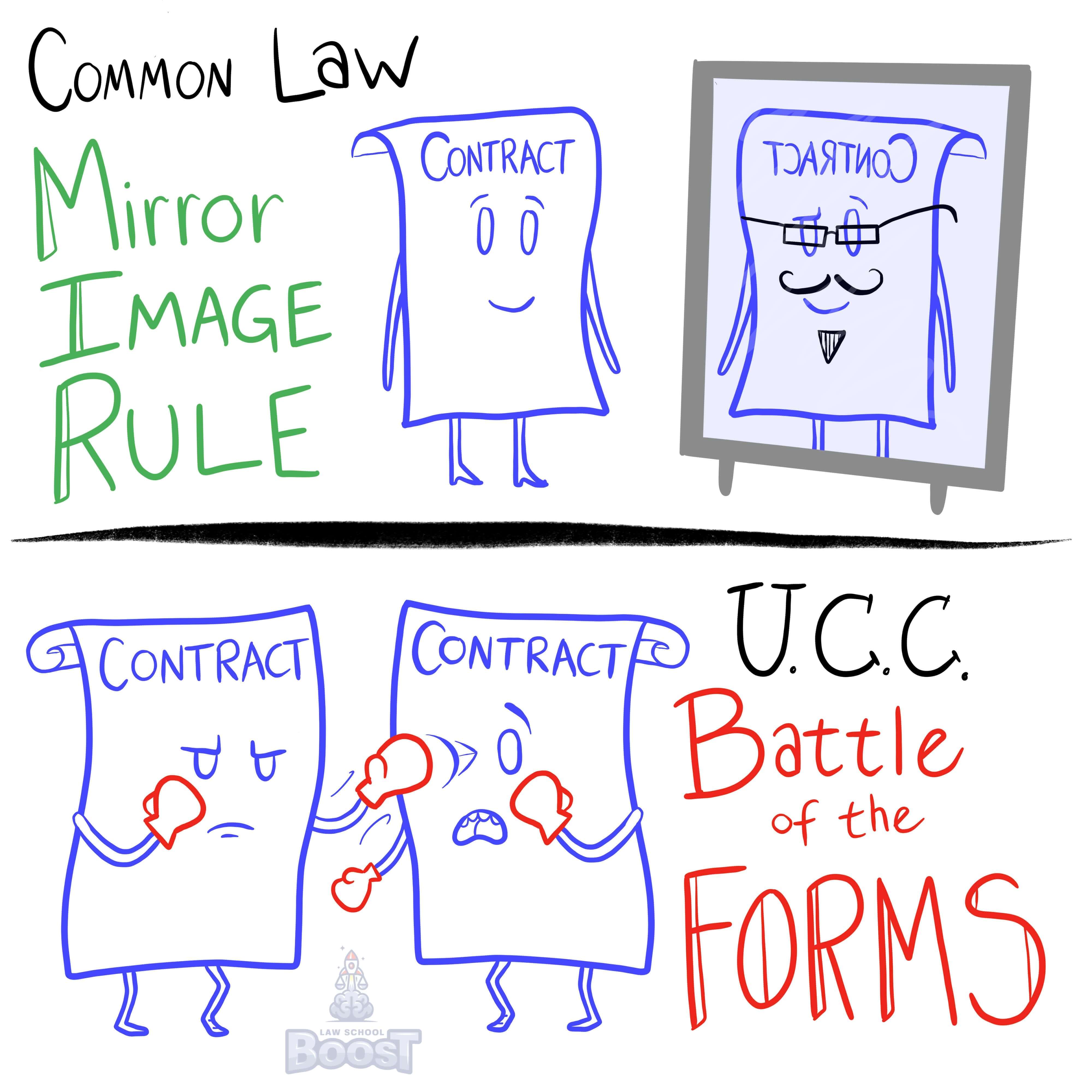
The first thing you'll notice about this answer is that it specifically applies to circumstances where at least one party is a non-merchant. This is important, because UCC has special rules for merchants vs. non-merchants, because it is generally less protective of merchants (since they are seen as being professionals who should know what they are doing, vs. non-merchants who are just everyday normal citizens trying to buy stuff they want).
In a scenario where at least one of the parties is a non-merchant, additional terms or different terms are considered "mere proposals". In other words, if someone doesn't want something, they should decline the offer. If they accept the offer while trying to add new terms, those terms are non-binding suggestions that may be ignored by the offeror.
In a scenario where at least one of the parties is a non-merchant, additional terms or different terms are considered "mere proposals". In other words, if someone doesn't want something, they should decline the offer. If they accept the offer while trying to add new terms, those terms are non-binding suggestions that may be ignored by the offeror.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Bob sends an email to Sam offering to sell his iPhone for $500. Sam responds, "I accept. Please ship it to me today so that I receive it no later than Friday." Result: First, note that neither Bob or Sam are merchants. Second, note that Sam accepted the original offer, and then included additional terms that require Bob to ship it to the same day so that it is received no later than Friday. Under the UCC, Sam has legally accepted Bob's offer, but whether or not Sam's additional terms are binding on Bob will depend on how they are treated under the battle of the forms rules, which we'll discuss in later cards. For now, the purpose of this card is to make it clear that you need to be able to parse the difference between acceptances with additional terms, and counteroffers or conditional acceptances.
Hypo 2: Bob sends an e-mail to Sam offering to sell his iPhone for $500. Sam responds, "I accept, so long as you can ship it today so it gets to me by Friday." Result: This is a conditional acceptance, which is a rejection of the original offer. If Bob chooses to ship it today so it gets to Sam by Friday, then this subsequent conduct can still create a contract, obligating Sam to pay $500. Likewise, if Bob accepts the payment of $500, that conduct would also create a contract based on these new terms.
Hypo 2: Bob sends an e-mail to Sam offering to sell his iPhone for $500. Sam responds, "I accept, so long as you can ship it today so it gets to me by Friday." Result: This is a conditional acceptance, which is a rejection of the original offer. If Bob chooses to ship it today so it gets to Sam by Friday, then this subsequent conduct can still create a contract, obligating Sam to pay $500. Likewise, if Bob accepts the payment of $500, that conduct would also create a contract based on these new terms.
Visual Aids

Related Concepts
Are offers assignable?
Are pre-existing duties valid consideration?
Can partial payment of a debt be consideration for release of that debt?
How can an offeree reject an offer?
How do courts assess the adequacy of consideration?
How may an offer be revoked?
Though offers can generally be freely revoked, what are the 4 exceptions?
Under battle of the forms, what happens to additional terms in an acceptance between two merchants?
Under battle of the forms, what happens to different terms in an acceptance between two merchants?
What are consideration substitutes?
What are illusory promises and how do they affect a contract?
What are requirement and output contracts?
What are the methods of terminating an offer?
What are the requirements of an offer?
What are the UCC Gap Fillers?
What is acceptance?
What is a contract?
What is a merchant's firm offer?
What is an option contract?
What is consideration?
What is detrimental reliance?
What is promissory estoppel?
What is required to form a valid, binding contract?
What is the effect of a conditional acceptance on an offer?
What is the effect of a contract that contains vague or ambiguous terms?
What is the effect of a contract that is missing price terms?
What is the effect of a contract that is missing quantity terms?
What is the effect of a counteroffer on an offer?
What is the effect of a lapse of time on an offer?
What is the effect of an offeree beginning to perform in response to an offer?
What is the effect of a seller sending non-conforming goods?
What is the effect of including additional or different terms to an offer?
What is the effect of part performance of a unilateral contract?
What is the effect of the death of a party prior to acceptance of an offer?
What is the Mailbox Rule and when does it apply?
When are advertisements valid offers?
When are price quotes valid offers?
When is past or moral consideration valid?
Who controls the method of acceptance, and what are the typical ways that an offer is accepted?


