🤔
Contracts • Contract Formation
K#031
Legal Definition
Additional terms become part of the contract unless they: (1) materially alter its original terms; or (2) the offeror has objected or objects within a reasonable time after notice; or (3) the offer expressly limits acceptance to the terms of the offer.
Plain English Explanation
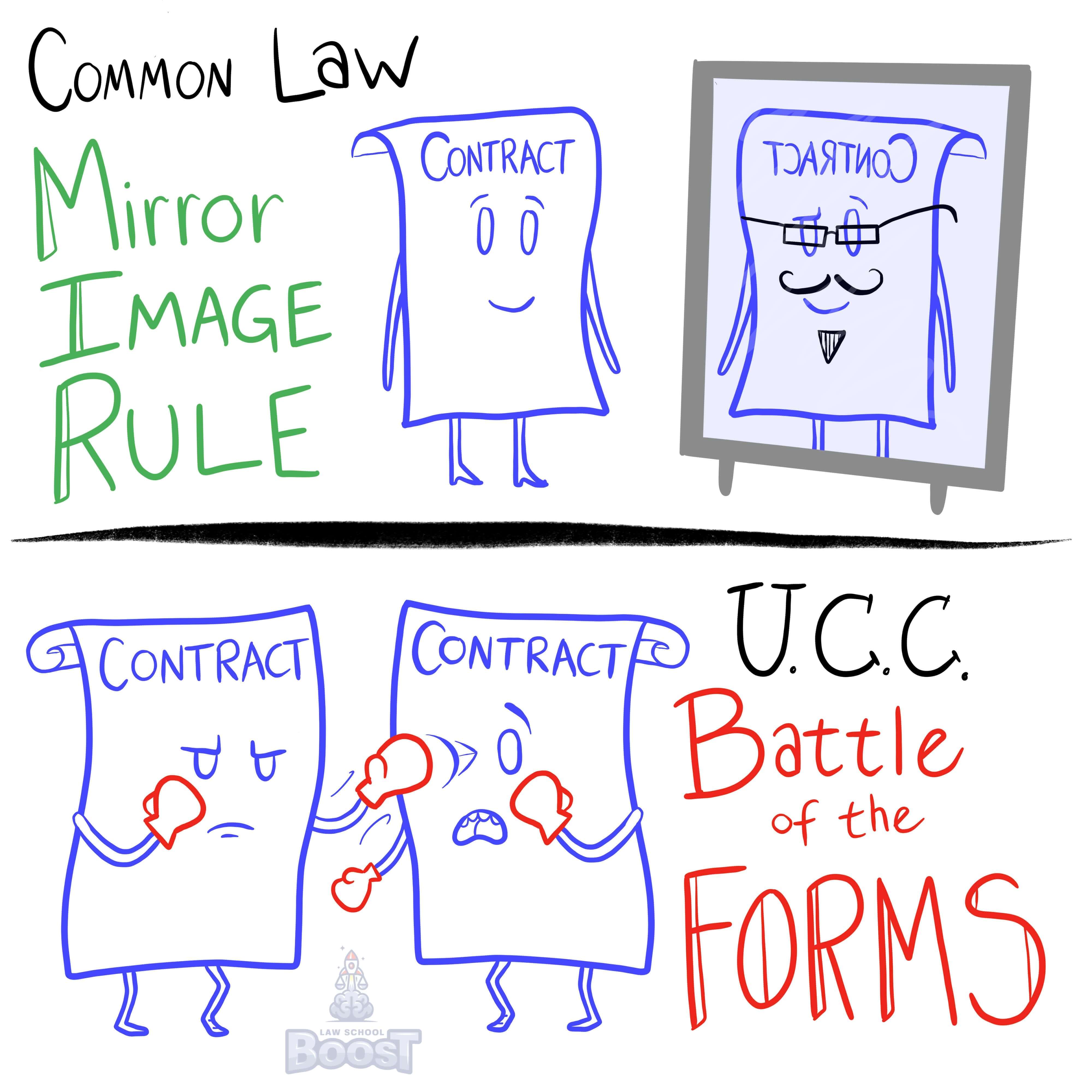
The first thing you'll notice about this answer is that it specifically applies to circumstances where both parties are merchants. This is important, because UCC has special rules for merchants vs. non-merchants, because it is generally less protective of merchants (since they are seen as being professionals who should know what they are doing, vs. non-merchants who are just everyday normal citizens trying to buy stuff they want).
In a scenario where both parties are merchants, additional terms will generally become part of the contract unless they fall into one of three exceptions:
The first exception is if the new terms materially alter the original terms of the contract. When things matter, they are material, so a material alteration is an alteration that matters, or is important enough to change the bargain. For example, if Bob offers to sell Sam a crate of widgets delivered to Sam's business, if Sam specifies that they must be delivered to the back door of the business, it's not really that big of a deal. Yes, it is a new term, and yes, it may take extra effort compared to delivering them to the front door, but it is unlikely to be considered material. As a result, Sam's terms will become part of the contract (unless one of the other exceptions apply). However, imagine if, instead, Sam specified that they must be delivered to his warehouse, located on the top of a mountain, accessible only by helicopter. That would be a pretty big change -- a material change, which means it would not become part of the contract.
The second exception is when the person making the offer has either objected to the proposed term at some point, or objects to it within a "reasonable time" after they have notice of the term. In other words, if Sam knows that Bob will not deliver to back doors of companies, then his proposal will not be added. Even though it isn't very material, Bob has objected to it in the past and it's not fair to assume he's okay with it now. Similarly, if Bob see's Sam's term of "deliver to my backdoor," he is able to object to it and cancel it out as long as he doesn't wait too long. How long is too long? That's for you to argue on the exam.
The third exception is when the offer itself expressly limits acceptances to the terms of the offer. In other words, where the offer very clearly states that no alterations are allowed, then they are not.
In a scenario where both parties are merchants, additional terms will generally become part of the contract unless they fall into one of three exceptions:
The first exception is if the new terms materially alter the original terms of the contract. When things matter, they are material, so a material alteration is an alteration that matters, or is important enough to change the bargain. For example, if Bob offers to sell Sam a crate of widgets delivered to Sam's business, if Sam specifies that they must be delivered to the back door of the business, it's not really that big of a deal. Yes, it is a new term, and yes, it may take extra effort compared to delivering them to the front door, but it is unlikely to be considered material. As a result, Sam's terms will become part of the contract (unless one of the other exceptions apply). However, imagine if, instead, Sam specified that they must be delivered to his warehouse, located on the top of a mountain, accessible only by helicopter. That would be a pretty big change -- a material change, which means it would not become part of the contract.
The second exception is when the person making the offer has either objected to the proposed term at some point, or objects to it within a "reasonable time" after they have notice of the term. In other words, if Sam knows that Bob will not deliver to back doors of companies, then his proposal will not be added. Even though it isn't very material, Bob has objected to it in the past and it's not fair to assume he's okay with it now. Similarly, if Bob see's Sam's term of "deliver to my backdoor," he is able to object to it and cancel it out as long as he doesn't wait too long. How long is too long? That's for you to argue on the exam.
The third exception is when the offer itself expressly limits acceptances to the terms of the offer. In other words, where the offer very clearly states that no alterations are allowed, then they are not.
Hypothetical
See Simple English Tab
Visual Aids

Related Concepts
Are offers assignable?
Are pre-existing duties valid consideration?
Can partial payment of a debt be consideration for release of that debt?
How can an offeree reject an offer?
How do courts assess the adequacy of consideration?
How may an offer be revoked?
Though offers can generally be freely revoked, what are the 4 exceptions?
Under battle of the forms, what happens to additional or different terms in an acceptance when at least one of the parties is a non-merchant?
Under battle of the forms, what happens to different terms in an acceptance between two merchants?
What are consideration substitutes?
What are illusory promises and how do they affect a contract?
What are requirement and output contracts?
What are the methods of terminating an offer?
What are the requirements of an offer?
What are the UCC Gap Fillers?
What is acceptance?
What is a contract?
What is a merchant's firm offer?
What is an option contract?
What is consideration?
What is detrimental reliance?
What is promissory estoppel?
What is required to form a valid, binding contract?
What is the effect of a conditional acceptance on an offer?
What is the effect of a contract that contains vague or ambiguous terms?
What is the effect of a contract that is missing price terms?
What is the effect of a contract that is missing quantity terms?
What is the effect of a counteroffer on an offer?
What is the effect of a lapse of time on an offer?
What is the effect of an offeree beginning to perform in response to an offer?
What is the effect of a seller sending non-conforming goods?
What is the effect of including additional or different terms to an offer?
What is the effect of part performance of a unilateral contract?
What is the effect of the death of a party prior to acceptance of an offer?
What is the Mailbox Rule and when does it apply?
When are advertisements valid offers?
When are price quotes valid offers?
When is past or moral consideration valid?
Who controls the method of acceptance, and what are the typical ways that an offer is accepted?


