😀
Real Property • Easements
PROP#124
Legal Definition
A license may become irrevocable: (1) by estoppel, if the licensee has substantially invested labor or capital in reliance of the license; or (2) where the license is coupled with an interest.
Plain English Explanation
A license to use someone’s property is usually something that can be taken back—kind of like borrowing someone’s bike. They can say, “Hey, I need it back,” and that’s that. But, there are situations where this permission, or "license," becomes irrevocable, meaning it can’t be taken away, and here’s how that happens.
(1) By estoppel: This is like when someone says, “Yeah, you can build a treehouse in my yard,” and you go all out—you spend money, time, and effort building the coolest treehouse ever. If the property owner suddenly says, “Actually, never mind, tear it down,” the law steps in and says, “Nope, they can’t do that.” Why? Because you relied on their promise and invested in it. The law doesn’t want to leave you hanging after you’ve made significant investments based on that permission.
(2) Coupled with an interest: This one is a little more technical, but think of it as having the right to use the property because you have some kind of stake in it. For example, if you bought a piece of timber on someone’s land, and they gave you permission to come and remove it, that permission (license) can’t just be revoked. It’s tied to your right to the timber, which is your “interest” in the property. So, as long as you still have that interest (the timber), you have the right to access the land to remove it.
(1) By estoppel: This is like when someone says, “Yeah, you can build a treehouse in my yard,” and you go all out—you spend money, time, and effort building the coolest treehouse ever. If the property owner suddenly says, “Actually, never mind, tear it down,” the law steps in and says, “Nope, they can’t do that.” Why? Because you relied on their promise and invested in it. The law doesn’t want to leave you hanging after you’ve made significant investments based on that permission.
(2) Coupled with an interest: This one is a little more technical, but think of it as having the right to use the property because you have some kind of stake in it. For example, if you bought a piece of timber on someone’s land, and they gave you permission to come and remove it, that permission (license) can’t just be revoked. It’s tied to your right to the timber, which is your “interest” in the property. So, as long as you still have that interest (the timber), you have the right to access the land to remove it.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Amy owns Whiteacre, a beautiful piece of property. Bob is getting married soon and asks Amy if he can host his wedding on Whiteacre. Amy agrees. Bob spends $10,000 on his wedding: hiring caterers, a tent company, rental chairs and tables, decorations, and custom wedding invitations with Whiteacre's address on it. A week before Bob's wedding, Amy says, "I've changed my mind. You can't have your wedding here." Result: Bob had a license to perform his wedding on Whiteacre. Even though Amy is generally allowed to revoke Bob's license at any point, because Bob has detrimentally relied on Amy's license and has invested a substantial amount of money and resources for his wedding, which it is now too late to reschedule, a court will likely hold that Amy is estopped from revoking Bob's license, and thus the license is irrevocable by estoppel.
Hypo 2: Amy owns Whiteacre where she is a beekeeper. Amy sells her honey in large barrels. Bob calls Amy and offers to buy 3 barrels of her honey. Amy accepts, processes Bob's payment over the phone, and says Bob can pick them up later that day from her barn on Whiteacre. A couple hours later, Amy changes her mind and tells Bob he is not allowed on Whiteacre. Result: When Bob purchased 3 barrels of honey from Amy, he had a license that gave him permission to enter Whiteacre in order to take possession of the 3 barrels. This interest makes his license irrevocable for a reasonable period of time required to enter Whiteacre in order to retrieve his purchased goods, which means Amy has no right to tell him he can no longer come onto Whiteacre.
Hypo 3: Amy has a bounce house on Whiteacre that she allows people to use from time to time. Bob loves bounce houses. Bob offers Amy $80 for 8 hours of time in her bounce house. Amy accepts. After 4 hours, Amy has gotten tired of Bob's loud giggling and laughter, so she kicks him off her property. Result: Bob has every right to sue Amy for the 4 hours of time he was denied to play in her bounce house, but the fact that he paid money doesn't mean his license was irrevocable.
Hypo 2: Amy owns Whiteacre where she is a beekeeper. Amy sells her honey in large barrels. Bob calls Amy and offers to buy 3 barrels of her honey. Amy accepts, processes Bob's payment over the phone, and says Bob can pick them up later that day from her barn on Whiteacre. A couple hours later, Amy changes her mind and tells Bob he is not allowed on Whiteacre. Result: When Bob purchased 3 barrels of honey from Amy, he had a license that gave him permission to enter Whiteacre in order to take possession of the 3 barrels. This interest makes his license irrevocable for a reasonable period of time required to enter Whiteacre in order to retrieve his purchased goods, which means Amy has no right to tell him he can no longer come onto Whiteacre.
Hypo 3: Amy has a bounce house on Whiteacre that she allows people to use from time to time. Bob loves bounce houses. Bob offers Amy $80 for 8 hours of time in her bounce house. Amy accepts. After 4 hours, Amy has gotten tired of Bob's loud giggling and laughter, so she kicks him off her property. Result: Bob has every right to sue Amy for the 4 hours of time he was denied to play in her bounce house, but the fact that he paid money doesn't mean his license was irrevocable.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
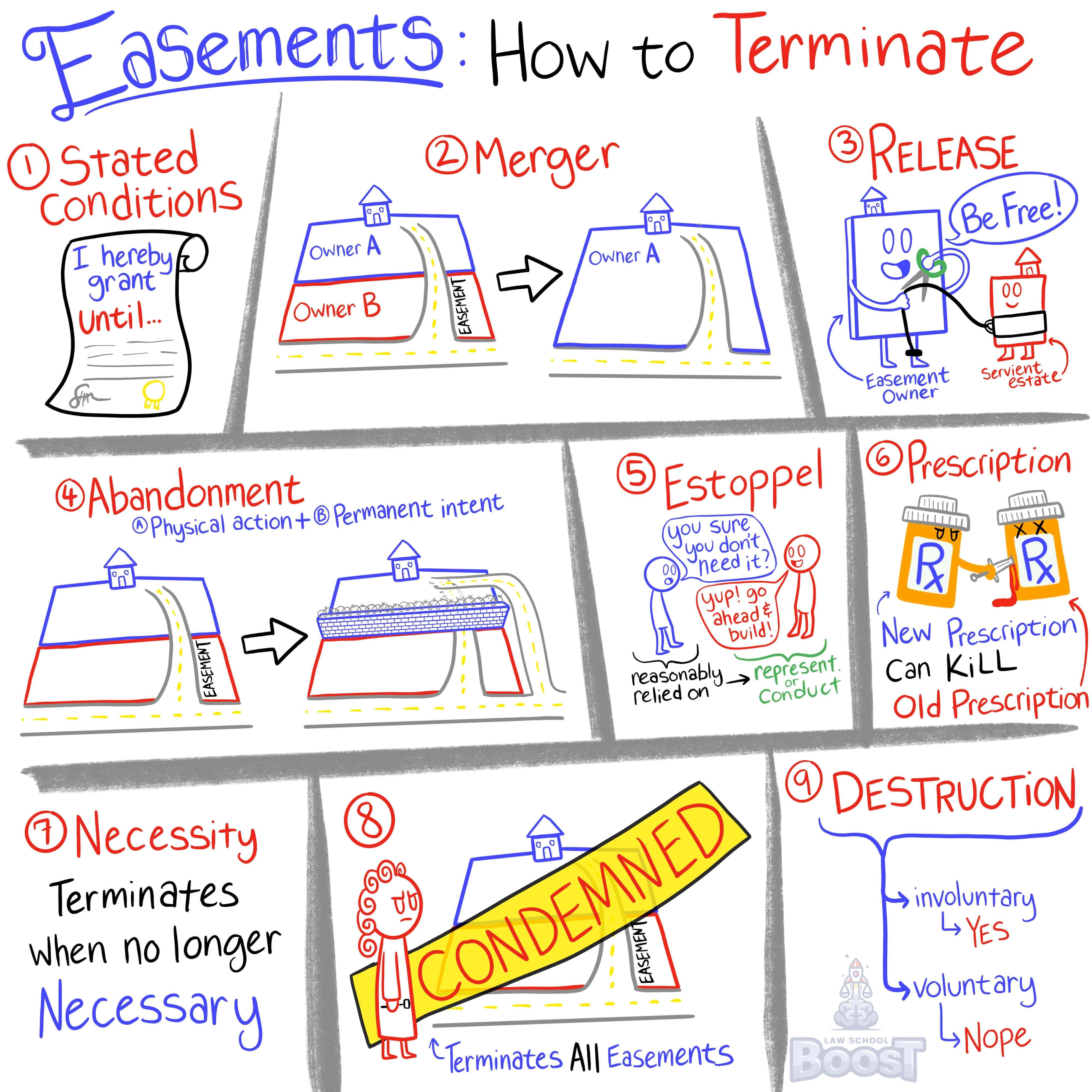
How can an easement be terminated?
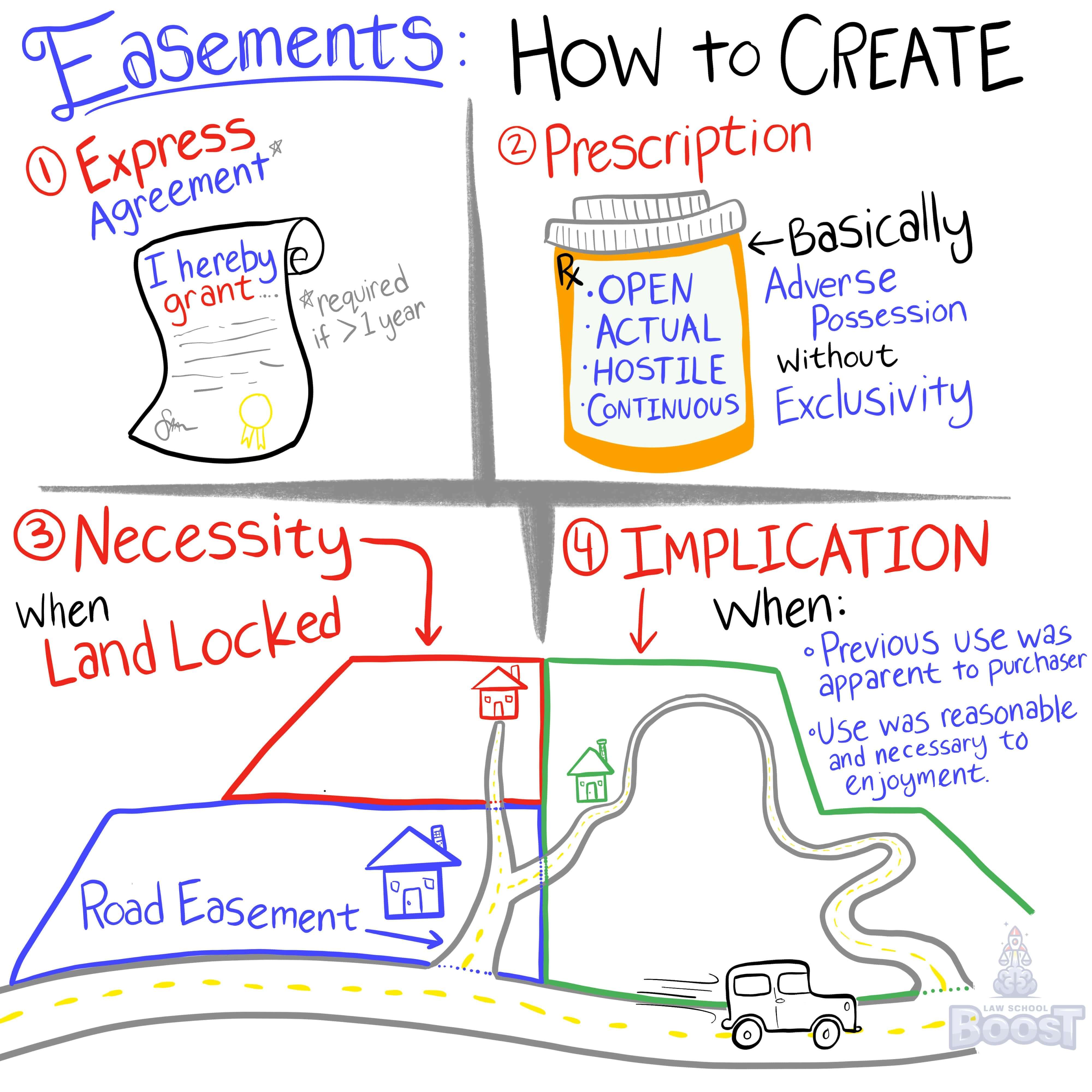
How is an easement created?
How is an easement terminated via abandonment?
How is an easement terminated via destruction or condemnation?
How is an easement terminated via estoppel?
How is an easement terminated via prescription?
How is an easement terminated via release?
How is an easement terminated via stated condition?
How is an easement terminated via unity of ownership?
If the holder of an easement misuses it, does the easement terminate?
In assessing an easement, who has a duty to make repairs?
In assessing a property law issue, what is a license?
What constitutes a valid easement by express grant?
What is an affirmative easement?
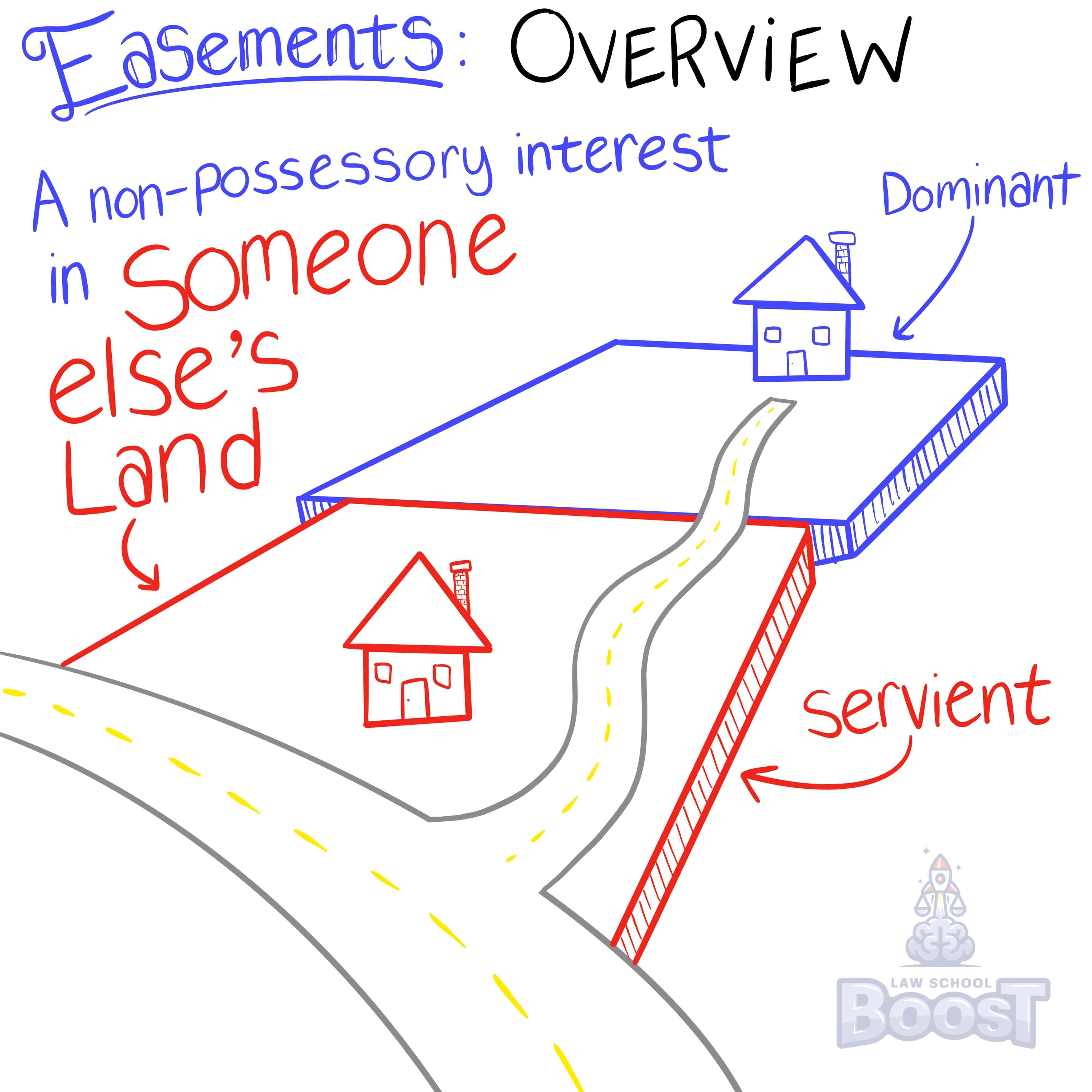
What is an easement?
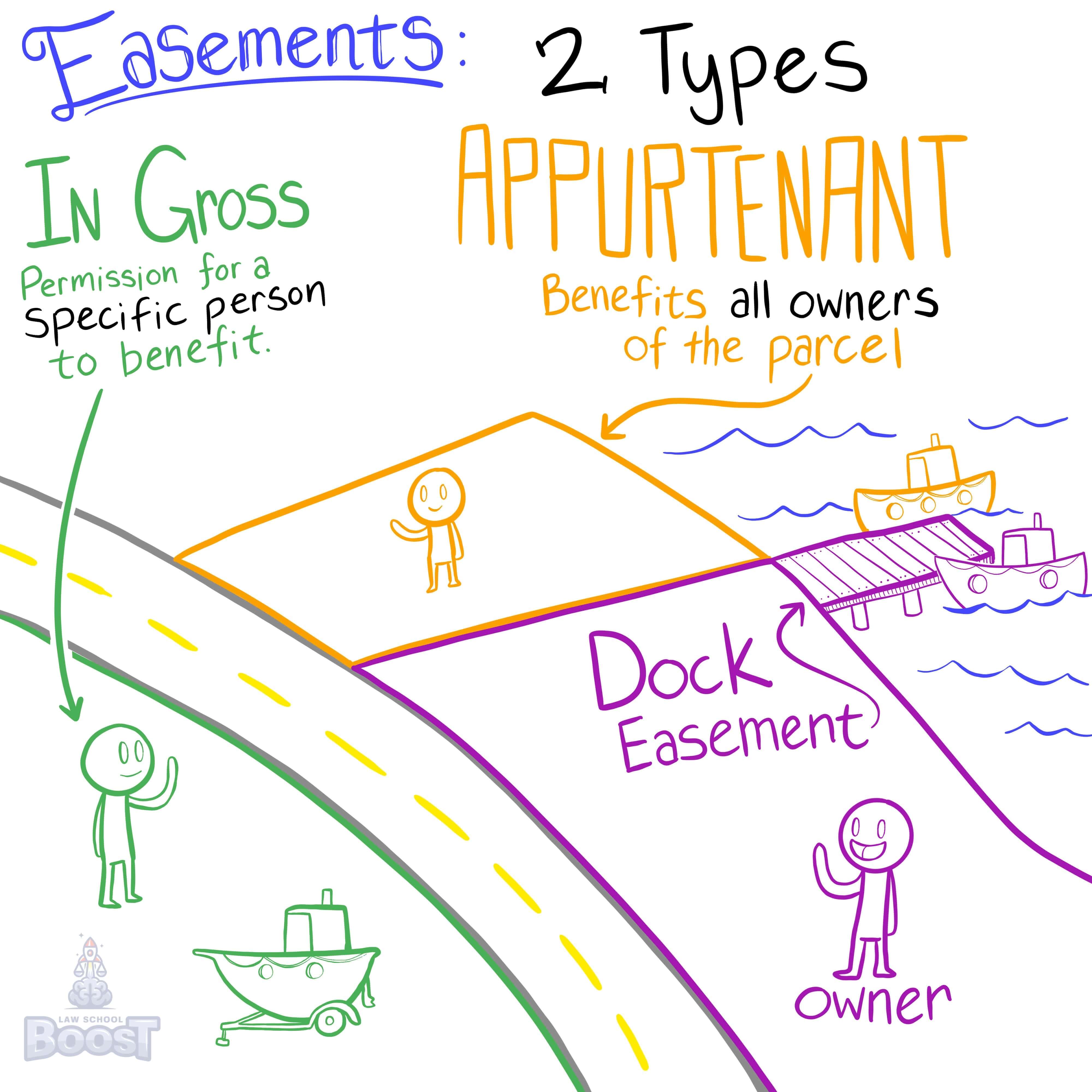
What is an easement appurtenant?
What is an easement by prescription and how is it acquired?
What is an easement in gross?
What is a negative easement?
What is the difference between a license and an easement?
What is the result of a failed attempt to create an easement?
When does an easement by express reservation arise?
When does an easement by necessity arise?
When does an easement by necessity terminate?
When may an easement be implied without preexisting use?
When may existing use create an implied easement?


