Unpublished Flashcard
This flashcard is not publicly visible and is only accessible to admin users.
🤝
Contracts • Remedies for Unexcused Non-Performance
REM#052
Legal Definition
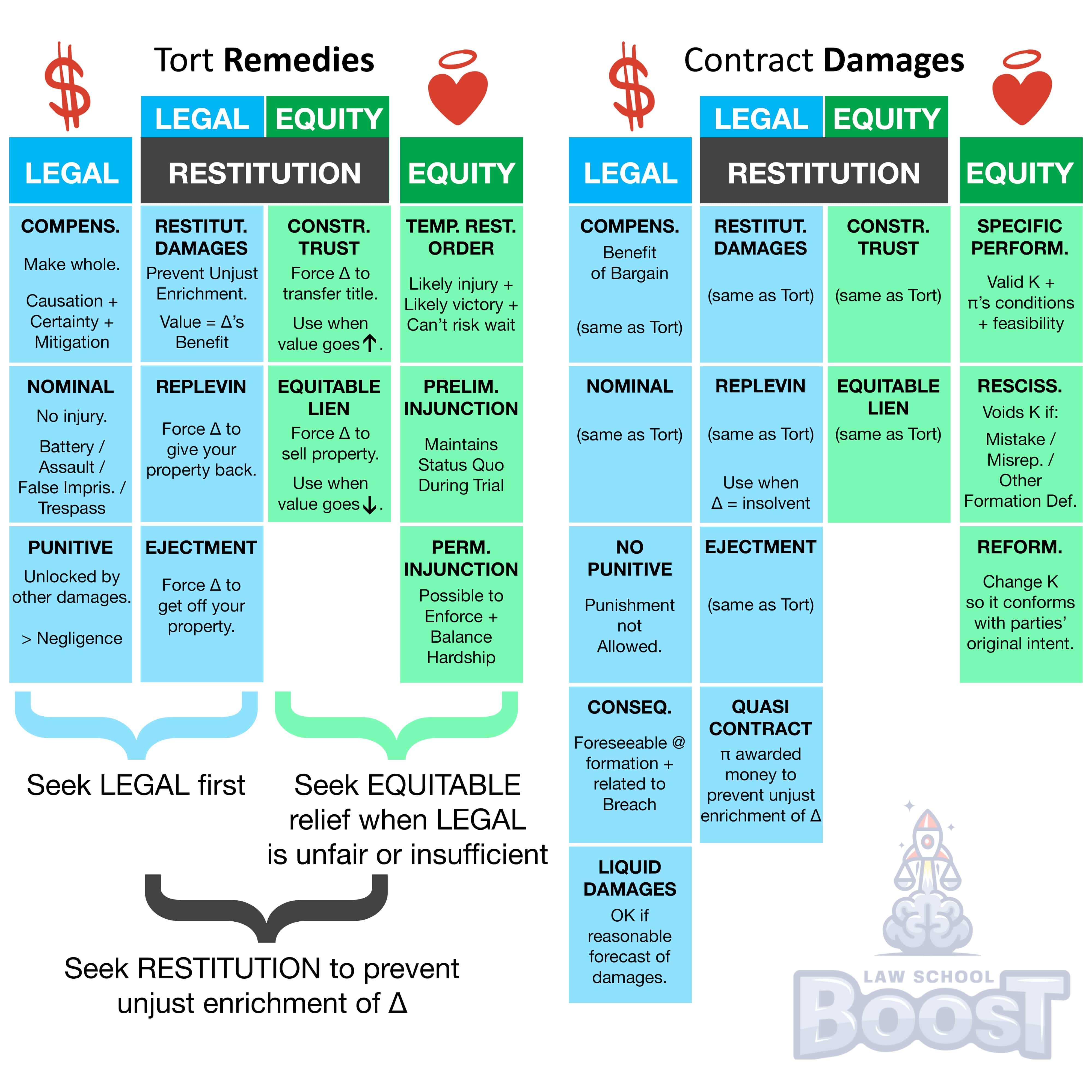
Specific performance is a remedy where the court orders a defendant to perform the contract.
To successfully seek specific performance, a plaintiff must show (1) the contract is valid (i.e., certain and definite); (2) the plaintiff's contract conditions have been satisfied; (3) the plaintiff has no adequate legal remedy; and (4) enforcement is feasible.
To successfully seek specific performance, a plaintiff must show (1) the contract is valid (i.e., certain and definite); (2) the plaintiff's contract conditions have been satisfied; (3) the plaintiff has no adequate legal remedy; and (4) enforcement is feasible.
Plain English Explanation
Imagine you and a friend made a promise to trade toys, but then your friend backs out. Instead of giving you another toy or money as an apology, you just want the original toy you were promised. In the legal world, if someone doesn't do what they promised in a contract, the court can step in and say, "Hey, you need to do exactly what you promised." But there are rules! The person asking for this has to prove a few things:
(1) The promise (or contract) was clear and real.
(2) They did their part of the deal.
(3) Money or another toy won't fix the problem.
(4) It's possible to make the other person do what was promised.
#4 is super important. Since the 13th Amendment of the Constitution abolishes slavery, courts do not have the power to force someone to work against their will even if their labor is what was bargained for in the contract. In such cases, courts will prefer to award monetary damages to enable the plaintiff to find someone else to engage with.
(1) The promise (or contract) was clear and real.
(2) They did their part of the deal.
(3) Money or another toy won't fix the problem.
(4) It's possible to make the other person do what was promised.
#4 is super important. Since the 13th Amendment of the Constitution abolishes slavery, courts do not have the power to force someone to work against their will even if their labor is what was bargained for in the contract. In such cases, courts will prefer to award monetary damages to enable the plaintiff to find someone else to engage with.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Bob sells a unique, one-of-a-kind painting to Sam and promises to deliver it. After receiving payment, Bob refuses to give the painting to Sam. Result: The court orders Bob to give the painting to Sam because money can't replace this unique item, and Sam has already paid for it.
Hypo 2: Bob agrees to sell a piece of land to Sam. After Sam pays, Bob refuses to transfer the land's title. Result: The court makes Bob transfer the title to Sam because land is unique, and giving money back isn't the same as getting the land.
Hypo 3: Sam wants to hire Elon Musk to come to their birthday party and tell jokes. Sam and Musk enter into a contract. However, a week before Sam's birthday party, Musk tells Sam that he is unable to attend the birthday party. Sam sues and seeks specific performance. Result: Even though Sam and Musk had a valid contract, a court will not be willing to force Musk to show up at an event they no longer wish to be present at. As a result, the court will likely opt to award Sam with monetary damages so Sam can hire a different clown.
Hypo 2: Bob agrees to sell a piece of land to Sam. After Sam pays, Bob refuses to transfer the land's title. Result: The court makes Bob transfer the title to Sam because land is unique, and giving money back isn't the same as getting the land.
Hypo 3: Sam wants to hire Elon Musk to come to their birthday party and tell jokes. Sam and Musk enter into a contract. However, a week before Sam's birthday party, Musk tells Sam that he is unable to attend the birthday party. Sam sues and seeks specific performance. Result: Even though Sam and Musk had a valid contract, a court will not be willing to force Musk to show up at an event they no longer wish to be present at. As a result, the court will likely opt to award Sam with monetary damages so Sam can hire a different clown.
Visual Aids