🌕
Corporations • Rights of Shareholders
CORP#048
Legal Definition
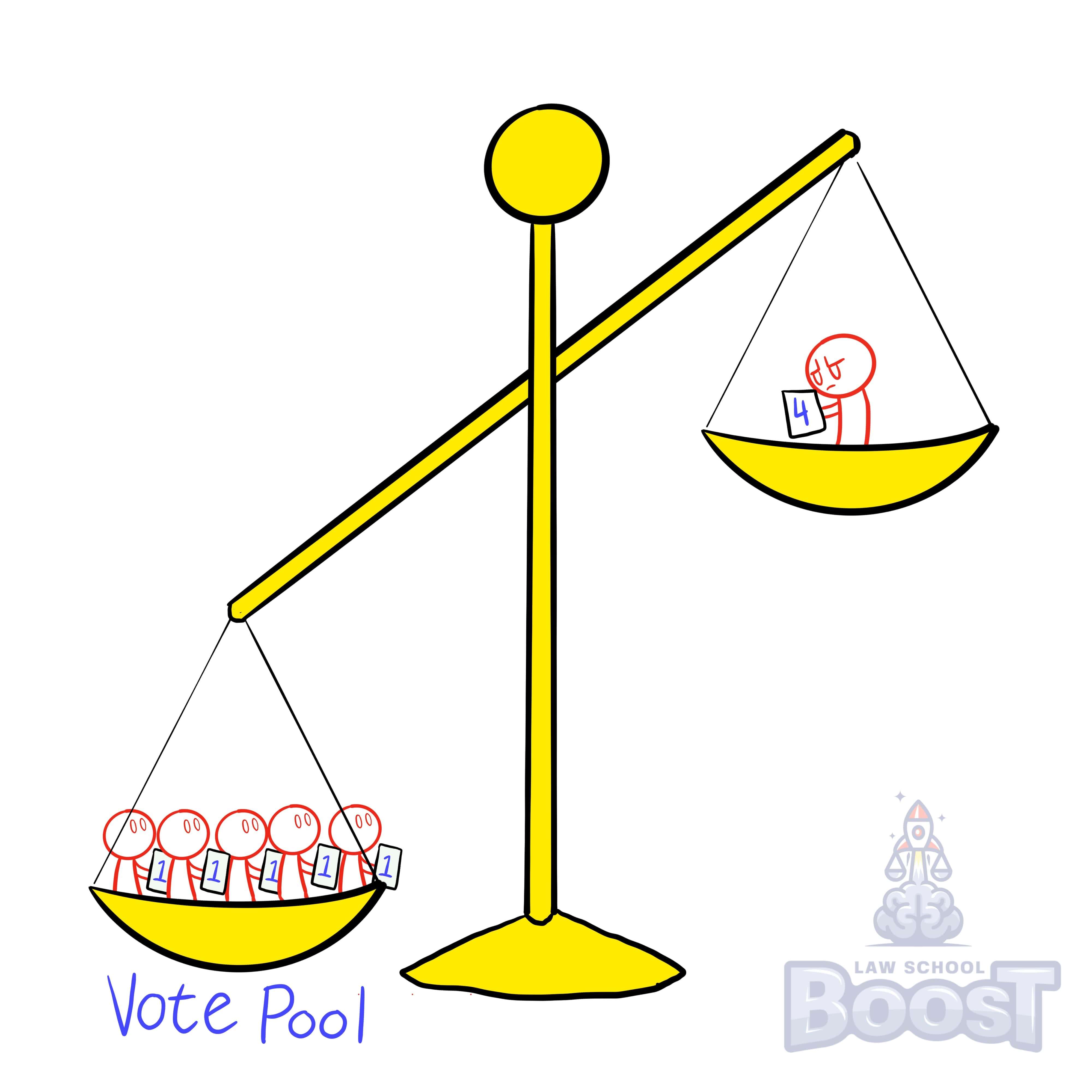
Shareholders who own relatively few voting shares may decide to increase their influence by agreeing to vote alike, via a voting trust or shareholder voting agreement.
Plain English Explanation
"Pooled voting" and "block voting" are like shareholder unions. It enables minority shareholders—who own so little of the company that they risk being pushed around—to team up with other shareholders to combine their votes and magnify their collective voice. This is accomplished through either a vote trust or a shareholder voting agreement.
A voting trust is a formal written agreement that gives voting power to a trustee, and is enforceable for up to 10 years.
A shareholder voting agreement is an agreement in writing to vote shares as required by the agreement, and is binding and enforceable on all signers.
A voting trust is a formal written agreement that gives voting power to a trustee, and is enforceable for up to 10 years.
A shareholder voting agreement is an agreement in writing to vote shares as required by the agreement, and is binding and enforceable on all signers.
Visual Aids
Related Concepts
Are shareholder proxies revocable?
How is an action approved at a shareholder meeting?
In regards to shareholder suits, what are derivative action?
In regards to shareholder suits, what are direct actions?
In what form may dividends be paid?
What are the liabilities of shareholders and controlling shareholders?
What are the minimum meeting requirements for a corporation?
What are the requirements for a shareholder to examine books and records?
What are the requirements for calling a special shareholder meeting?
What are the three most common forms of distributions?
What are the traditional limitations on distributions?
What are the ways in which a corporation may restrict the transfer of shares?
What is a professional corporation and how does it form?
What is a redemption right?
What is the difference between traditional voting and cumulative voting?
What is the priority of distribution for dividends?
What is the procedure for a shareholder to bring a derivative action?
What is the procedure for a shareholder to vote by proxy?
When and how may shareholders eliminate corporate formalities?
When can or can't a board of directors declare a distribution?
Who has the right to vote at a shareholder meeting?


