Unpublished Flashcard
This flashcard is not publicly visible and is only accessible to admin users.
🤝
Contracts • Excuse of Non-Performance
REM#050
Legal Definition
If the plaintiff is the breaching party, under the traditional view they cannot recover at all. However, under the modern view, they can recover the value of the benefit conferred, but the recovery cannot be greater than the contract rate, and it is reduced by ay damages suffered by the defendant as a result of the breach.
Plain English Explanation
When two people make a deal (a contract), and one person doesn't do what they promised (breaches the contract), the person who broke the promise might want to get something in return for what they did do. In the past, the person who broke the promise couldn't get anything. But nowadays, they can get something back, but only up to what was originally agreed upon in the deal. However, if the other person was hurt because of the broken promise, the amount the person who broke the promise gets is reduced.
Hypothetical
Hypo 1: Bob agrees to paint Sam’s house for $5,000. Bob finishes half of the job and then quits. Sam has to pay another painter $3,000 to finish the work. Bob sues Sam for the value of the work he did. Result: Under the modern view, Bob can recover the value of the work he did, but it will be reduced by the $3,000 Sam had to pay to finish the job. So, Bob may recover $2,000.
Hypo 2: Bob contracts to deliver 100 chairs to Sam’s restaurant for $10,000. Bob delivers only 50 chairs and then stops. Sam finds another supplier to deliver the remaining 50 chairs at an additional cost of $6,000. Bob sues Sam for payment for the 50 chairs he delivered. Result: Bob can recover the value of the 50 chairs he delivered, but Sam can reduce that amount by the $6,000 extra she had to pay, meaning Bob might not recover anything.
Hypo 2: Bob contracts to deliver 100 chairs to Sam’s restaurant for $10,000. Bob delivers only 50 chairs and then stops. Sam finds another supplier to deliver the remaining 50 chairs at an additional cost of $6,000. Bob sues Sam for payment for the 50 chairs he delivered. Result: Bob can recover the value of the 50 chairs he delivered, but Sam can reduce that amount by the $6,000 extra she had to pay, meaning Bob might not recover anything.
Visual Aids
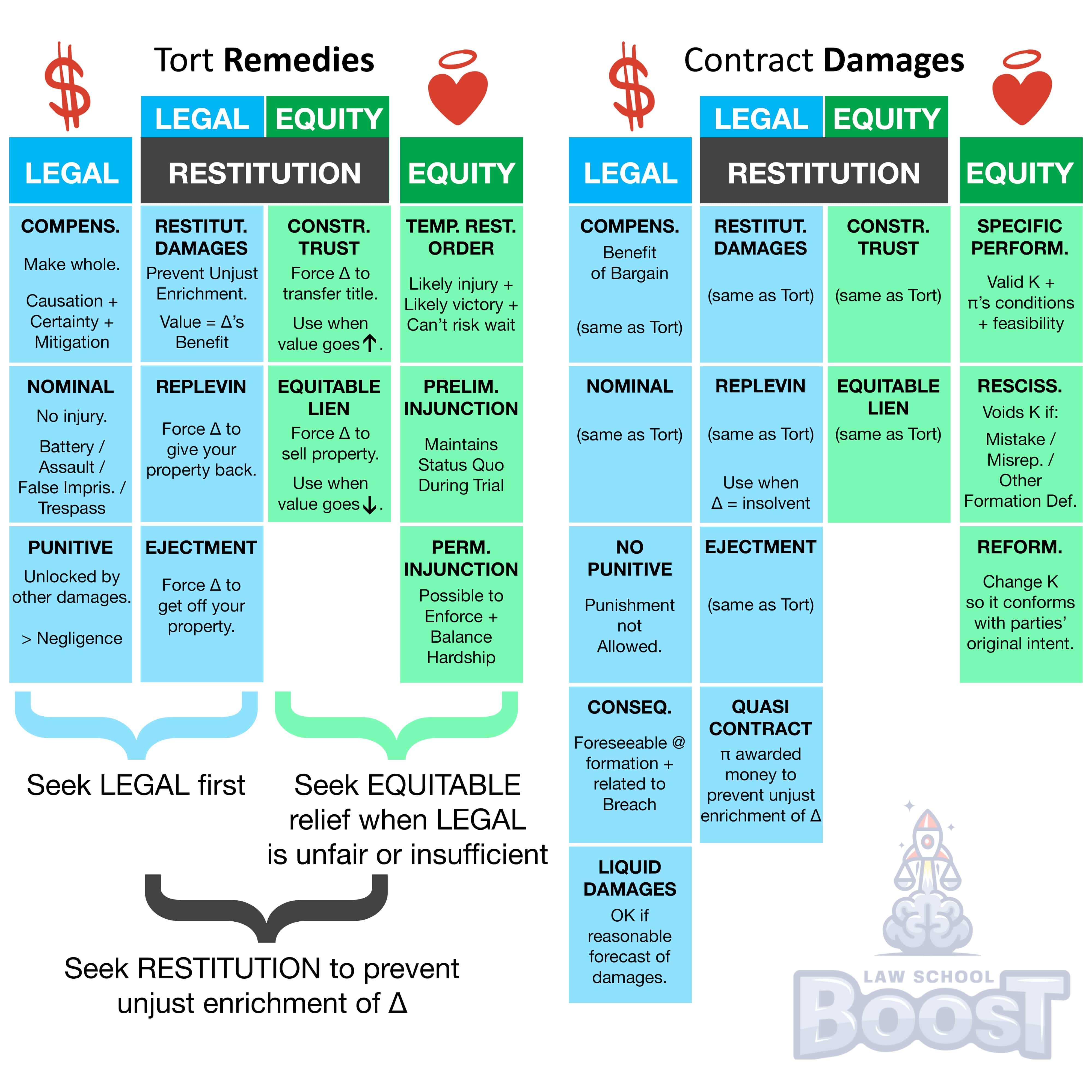
Related Concepts
How is performance affected when the subject matter of the contract is damaged or destroyed?
Under common law, is late performance a material breach?
Under common law, when is counter-performance excused?
Under common law, when may a breaching party recover in a divisible contract?
Under contract law, what is a modification?
What is excuse due to anticipatory repudiation?
What is excuse due to improper performance?
What is frustration of purpose?
What is impracticability?
What is the doctrine of impossibility?
What level of compliance is required to satisfy an express condition?
What options does the non-breaching party have in response to an anticipatory repudiation?


